
views
X
Research source
- Place a candle on a standing rod and secure 3 oz (100 ml) of water in a tin can 2 in (5 cm) above it. Light the candle.
- Measure the water temperature and candle weight. Then, use the formula q = Cp * m * (delta) t to calculate the heat liberated.
- Or, write the equation for combustion: 2NO + O2 = 2NO2. Add the enthalpies for the reactants and product and then subtract them.
Calculating Heat of Combustion Experimentally
Position the standing rod vertically. To begin setting up your experiment you will first place the rod on your work table.
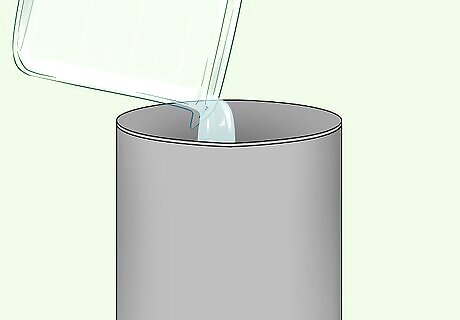
Measure 100ml of water into the tin can.
Put the substance at the base of the standing rod.
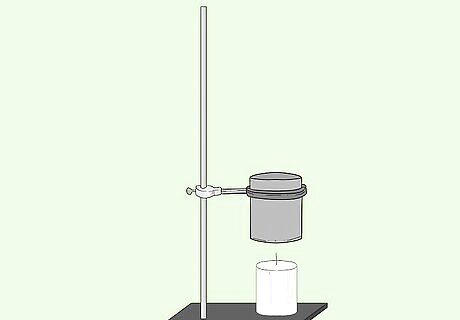
At 5cm above the substance affix the tin can with a clamp to the rod.
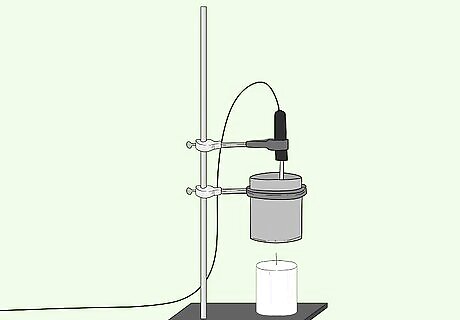
Affix the thermometer so that it is in the tin can but not touching the bottom base.
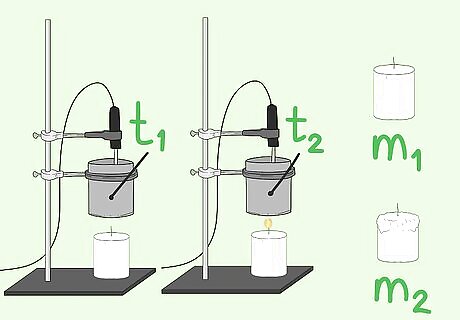
Experimentation Measure the temperature of the water and note it in degrees celsius. Measure the mass of the candle and note it in g. Light the substance. When the temperature of the water reaches 40 degrees Centigrade, blow out the substance. Measure the mass of the candle after burning and note it.

Calculation Use the formula q = Cp * m * (delta) t to calculate the heat liberated which heats the water. The specific heat Cp of water is 4.18 J/g C Mass of the water is 100g Delta t is the difference between the initial starting temperature and 40 degrees centigrade. Subtract the initial temperature of the water from 40 C. Substitute it into the formula and you will get the answer q in J. Convert into kJ by dividing q by 1000. Find the amount of substance burned by subtracting the final mass from the initial mass of the substance in g. Divide q in kJ by the mass of the substance burned. The answer is the experimental heat of combustion in kJ/g.
Calculating the Heat of Combustion Using Hess' Law
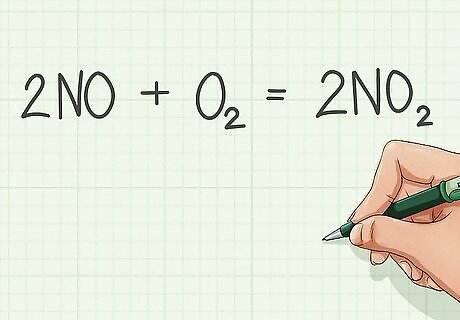
Write the balanced equation of combustion of the substance.

Find the enthalpies of formation for the reactants and add them. Enthalpies of formation are usually found in a table from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics.
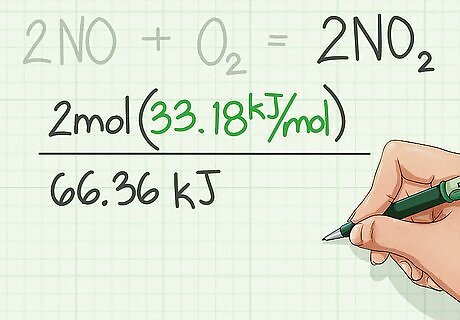
Find the enthalpies of formation of the products and add them. Use the table
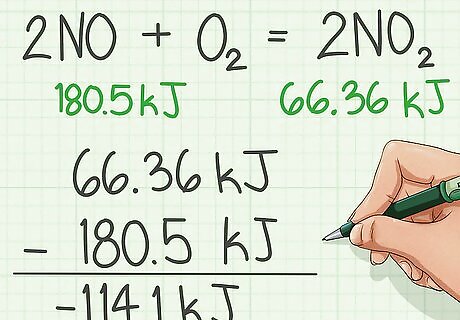
Subtract the enthalpies of the reactants from the product.
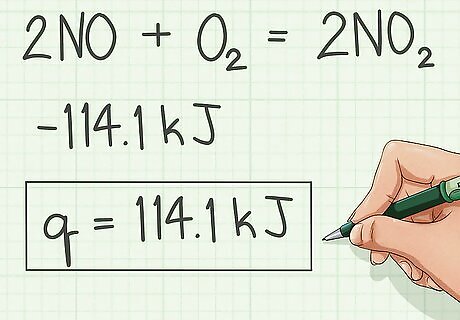
Switch the sign and that is the Heat of Combustion.



















Comments
0 comment