
views
For Tuition Purposes

Establish a domicile in Texas. The easiest way to establish a domicile is to own or rent a home somewhere within the state. If you're living with your parents, that would typically mean that they own or rent a home in Texas. Generally, this needs to be your primary residence—in other words, the place where you live most of the time, not a summer or vacation home. Employment is an important part of establishing a domicile. Either you (or your parents, if you're a dependent) must be gainfully employed in Texas in addition to owning or renting a home. If you are unhoused, talk to staff at a local shelter. They can complete an affidavit verifying your state residency.
Live in Texas for at least 12 months if you aren't a dependent. The clock counts backward from the official enrollment date for the year when you want to start school (also called the "census date"). Your 12 months must be continuous—you can leave the state to visit people or go on vacation, but you have to keep your home in Texas and have an intent to return. Intent is important when it comes to establishing residency for tuition purposes. No one's going to ask you to prove this one way or the other, but technically, you don't qualify for in-state tuition if you move to the state solely for the purpose of attending a state college or university as an in-state student. As an independent student, you typically also have to be able to show that you've been gainfully employed in the state (not including student employment) and have bills coming to you in your name at your Texas address.

Graduate from a Texas high school if you are a dependent. If you still live with your parents and they still claim you as a dependent on their taxes, you're typically looking at qualifying for in-state tuition as a dependent student. The easiest way to do this is to graduate from a Texas high school, as long as you lived in Texas for the 36 months immediately before high school graduation. You can also establish residency by taking the GED in Texas, but this is a double-edged sword since you have to show proof of residency to take the GED. If only one of your parents lives in Texas and the court granted them custody of you, you qualify as a Texas resident for tuition purposes as long as they didn't seek custody for the sole purpose of making you eligible for in-state tuition.

Provide proof of residency to your school's registrar. Typically, you'll answer some questions from your school's registrar's office. The registrar uses the information you provide to determine if you're eligible for the in-state tuition rate. Documents you can use to validate your answers to these questions include: A mortgage statement or lease Utility bills with your full name and address (or a parent's full name) A state identification card or driver license with your full name and address Texas car registration A visa, green card, or other immigration paperwork (other than a student visa)
For Tax or Legal Purposes

Buy or rent a home in Texas with the intent to stay there. As in other situations, intent is important here. You can only claim Texas residency for tax or legal purposes if the place where you live in Texas is the place you intend to make your home. That is, you plan on living there indefinitely, not for a limited time. When you're talking about taxes and courts, it doesn't matter how much of the year you live in Texas, only that you intend for that to be your residence. For example, you're a Texas resident if you consider your parents' home in Texas your home even though you spend most months of the year in school in another state. If you're unhoused, staff at the nearest shelter can help you establish your residency. Typically, they'll include the address of the shelter as your mailing address and complete an affidavit on your behalf.
Change your address with your employer and your financial institution. Changing your address with your employer and your financial institution signals that you intend to be taxed as a Texas resident. Texas doesn't have state income tax, so if you're moving from a state that does, make sure you do this as soon as possible. Working and banking in the state is one of the primary ways to establish that you're a legal resident of Texas, regardless of your purposes for doing so. Doing this also means your Texas address will be printed on your bank statements and pay stubs, which you can use as proof of residency.

Register your vehicle in Texas. If you have a vehicle that's registered in another state, you can leave it that way if you don't intend to stay in Texas indefinitely. But if you want to make Texas your legal home, get Texas tags on your car within 60 days of making the move. Before you get your vehicle registered and titled in Texas, you'll also need to change your residence with your car insurance company. To register your vehicle, you have to show proof that you carry car insurance that meets the state's minimum coverage requirements.

Cut ties completely with your previous state of residence. The more ties you continue to have with the state where you lived before, the more difficult it will be for you to convince legal authorities that you intend to make your home in Texas. How you cut these ties depends on what you still have connecting you to another state. For example, if you own property in another state, you might need to sell that or lease it out to a tenant to make it apparent that you don't intend to move back there. Other things you might do to cut ties include getting a local bank account, registering to vote with your new address, or registering your car from your new address. Cutting ties with your previous state is especially important for military folks stationed in Texas. If you don't cut ties with your previous state, you'll likely still be considered a resident of that state and not the state of Texas.

Fill out an affidavit if you're active-duty military. If you're ordered to a base in Texas and want to change your state of legal residence, it's not quite as simple as just filling out a change of address card. That's because orders to a new duty station don't change your state of legal residence. Instead, you have to send a letter to your former state's Income Tax Commission indicating your intent to become a legal resident of Texas. Information you could offer as proof of this intent includes: Titling and registering your vehicles in Texas Selling any property you own in the previous state where you lived Registering your children for school in Texas Living continuously in Texas Getting a Texas driver license Paying personal or real property taxes in Texas Becoming a member of religious or civic organizations in Texas

Live in Texas for at least 6 months if you plan to file for divorce. When you file for divorce, one of the facts you're required to plead is that you've lived in the state of Texas for at least 6 months before you filed the divorce action. Easy enough, but you also have to file in a county where you've lived for at least 90 days. This means that if you and your spouse separate and you move to the next county over, you'd need to live there for at least 3 months before you'd be able to file for divorce in that county. You could still file for divorce in the county where you previously lived, though. The clock starts ticking on the 6 months the moment you change your address on something official or sign a mortgage or lease agreement. This is why it's important to get your address changed as quickly as possible. The more places and ways you've listed your residence as an address in Texas, the more likely a court will consider you a Texas resident. If you meet these requirements, your spouse can also file for divorce in the county where you live, even if they don't live in Texas.
For Voting Purposes
Move to an address in Texas. You're technically eligible to vote in Texas from the first day you move to the state, assuming you move with the intention of living in the state indefinitely and making your home there. All you need to register is an address in the state where you receive mail. If you're unhoused, check at your local shelter—many of them allow you to use their address as a mailing address for voter registration and other purposes. A staff member will complete an affidavit certifying this.

Complete a voter registration application. Use Texas's online portal to fill out your voter registration application from the comfort of home. You can also fill out a voter registration application in person at your county's voter registrar office or public library, as well as many government offices and high schools. To vote in the next election, you have to submit your application within 30 days before the scheduled election day. If you're turning 18, you can submit your application before you turn 18 although you won't be eligible to vote until your birthday. Keep in mind that you have to be a U.S. citizen to vote in either federal or state elections in Texas.

Get an acceptable Texas identification card. While you don't necessarily have to show identification to register, you do need to have a valid photo identification with you when you go to vote at a Texas voting precinct. Acceptable identification includes: Texas driver license Texas Election Identification Certificate issued by the Texas Department of Public Safety (DPS) State personal identification card A military identification card that includes your photo and an address that matches the one on your voter registration A U.S. passport or citizenship certificate
Getting Texas State Identification
Change your address as soon as possible after you move to Texas. The easiest way to change your address for identification purposes is the US Postal Service change of address form. This form forwards mail from your old address to your new address so you'll get mail with your Texas address printed on it. If you are unhoused, a staff member at your nearest shelter can help you by filling out an affidavit to certify your residency in the state. Different shelters may have different requirements for this.
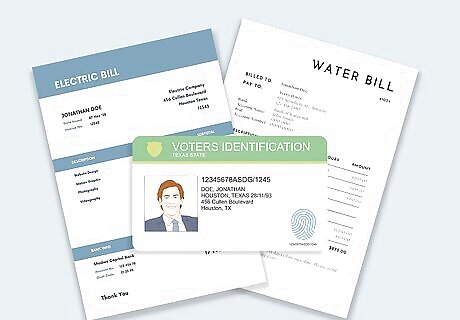
Save at least 2 printed documents to prove your residency. Generally, Texas accepts documents that have your full name and address printed (not handwritten) on them. Usually, a bill or statement you get in the mail from a company, government entity, or service provider is adequate. Examples of acceptable documents include: Utility bills Phone bills Current insurance policy statement or card Current deed, mortgage, mortgage statement, or residential lease agreement Valid, unexpired vehicle registration or title Valid, unexpired voter registration card Valid, unexpired Texas concealed handgun license or license to carry

Complete the driver license application. The Texas Department of Public Safety (DPS) requests that driver license applicants fill out their application online before they visit their nearest driver license office. This ensures that your information will be in the system when you arrive. The online application checklist also provides you with a list of documents you'll need to bring when you go to get your license.

Make an appointment at your nearest driver license office. Go online to the Texas DPS appointment scheduler to make your appointment. Driver license offices issue licenses by appointment only—they won't help you if you just walk in, even if you've already filled out the application online.

Provide documentation at your appointment. To get your driver license, you'll need to prove both your identity and your residency. You can typically prove your identity with a driver license from another state or a U.S. passport. The online application gives you a list of the specific documents you'll need based on the information you provide. If you're getting a driver license as opposed to a state identification card, you'll need to either present a valid unexpired license from another state or take the written and driving exams.


















Comments
0 comment