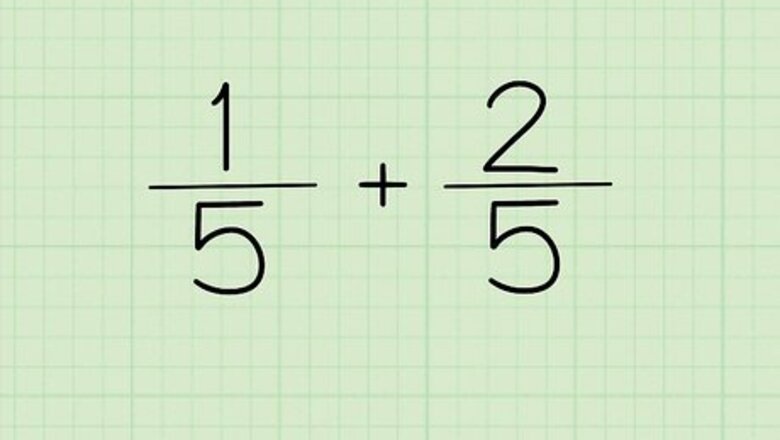
views
Adding and Subtracting Fractions with the Same Denominator
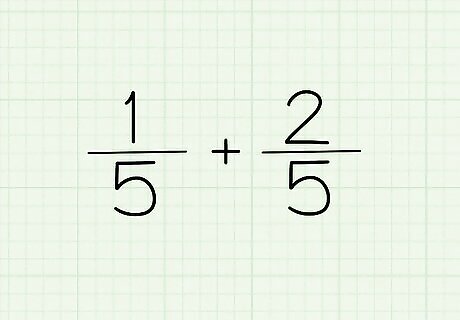
Write out your equation. If the denominator of the two fractions that you are adding or subtracting is the same, put the same number once as the denominator for your answer. In other words, 1/5 and 2/5 does not need to be written as 1/5 + 2/5 = ? It can be written as 1+2/5 = ?. The denominator is the same, so it can be written only once. Both numerators then go on top.
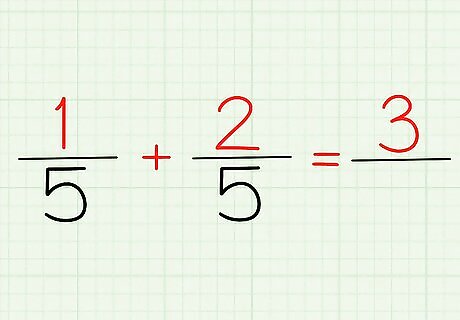
Add the numerators together. The "numerator" is the top number of any fraction. If we take the above example, 1/5 and 2/5, 1 and 2 are our numerators. Whether you have it written 1/5 + 2/5 or 1+2/5, you answer should be the same: 3! After all, 1 + 2 = 3.
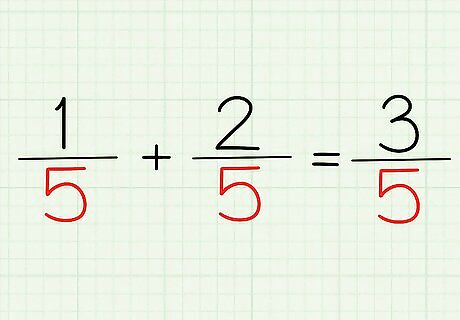
Leave the denominator alone. Since you're working with one constant denominator, don't do anything with it! Don't add, subtract, multiply, or divide. Just leave it be. So, using the same example, our denominator is 5. That's it! That's the bottom number of our fraction. That's half the answer already!
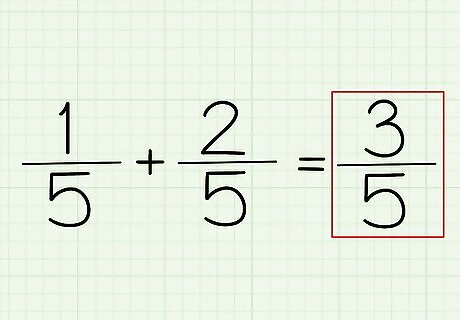
Come up with your answer. Now, all you do is write out your numerator and your denominator! If you've followed the above example, you'll find that the answer to this problem is 3/5. What was your numerator? 3. The denominator? 5. Therefore, 1/5 + 2/5, or 1+2/5, equals 3/5.
Adding and Subtracting Fractions with Different Denominators
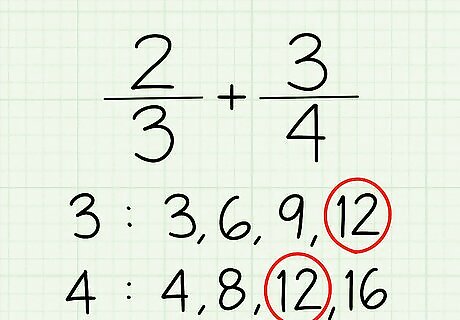
Find the lowest common denominator. This means the lowest number both denominators have in common. Let's take the fractions 2/3 and 3/4. What are the denominators? 3 and 4. To find the lowest common denominator of the two, you can do this one of three ways: Write out the multiples. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18...and so on. The multiples of 4? 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, etc. What's the lowest number seen in both of the sets? 12! That's your lowest common denominator, or LCD. Prime factorization. If you know what factors are, you can do prime factorization. That's finding out what numbers can make your denominators. For 3, the factors are 3 and 1. For 4, the factors are 2 and 2. Then, you multiply them together. 3 x 2 x 2 = 12. Your LCD! Multiply the numbers together for small numbers. In some cases, like this one, you could just multiply the numbers together – 3 x 4 = 12. However, if your denominators are big, don't do this! You don't want to multiply 56 x 44 and have to work with 2,464 as your answer!
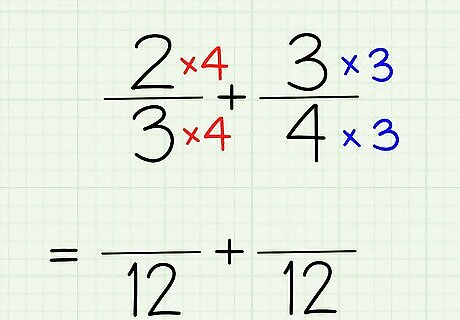
Multiply the denominator by the number needed to get the LCD. In other words, you want each of your denominators to be the same number – the LCD. In our example, we want our denominator to be 12. To turn 3 into 12, you need 3 x 4. To turn 4 into twelve, you need 4 x 3. The resulting like denominator will be the denominator for your final answer. So our 2/3 turns into 2/3 x 4 and 3/4 turns into 3/4 x 3. That means we now have 2/12 and 3/12. But we're not done yet! You'll notice that the denominators, in this instance, are multiplied by each other. This works in this situation, but not all situations. Sometimes, instead of multiplying the two denominators together, you can multiply both denominators by different numbers to get one small number. And then in other cases, sometimes you only have to multiply one denominator to make it equal to the denominator of the other fraction in the equation.
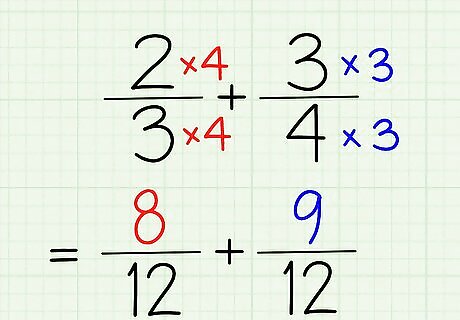
Multiple the numerator by that number, too. When you multiply the denominator by a certain number, you also have to multiply the numerator by the same number. What we did in the last step was just half of the multiplication necessary. We had 2/3x4 and 3/4x3 as our first step – to add the second step, it's really 2 x 4/3 x 4 and 3 x 3/4 x 3. That means our new numbers are 8/12 and 9/12. Perfect!
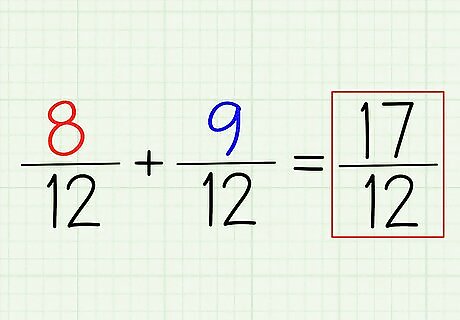
Add (or subtract) the numerators to get your answer. To add 8/12 + 9/12, all you have to do is add the numerators. Remember: you leave the denominator alone now. The number you got with the LCD is your final denominator. For this example, (8+9)/12 = 17/12. To turn this into a mixed fraction, simply subtract the denominator from the numerator and see what's left over. In this case, 17/12 = 1 5/12
Adding and Subtracting Mixed and Improper Fractions
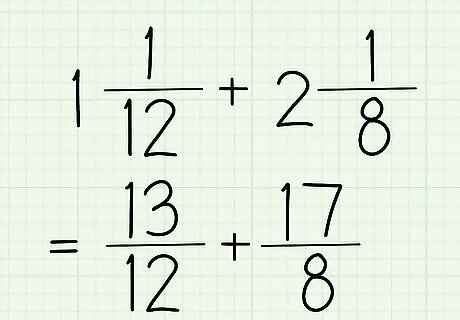
Convert your mixed fractions into improper fractions. A mixed fraction is when you have a whole number and a fraction, like in the above example (1 5/12). Meanwhile, an improper fraction is one where the numerator (the top number) is bigger than the denominator (the bottom number). That's also seen in the above step, with 17/12. For the example for this section, let's work with 13/12 and 17/8.

Find the common denominator. Remember the three ways you can find the LCD? By either writing out the multiples, using prime factorization, or by multiplying the denominators. Let's figure out the multiples of our example, 12 and 8. What's the smallest number these two go into? 24. 8, 16, 24 and 12, 24 – bingo!
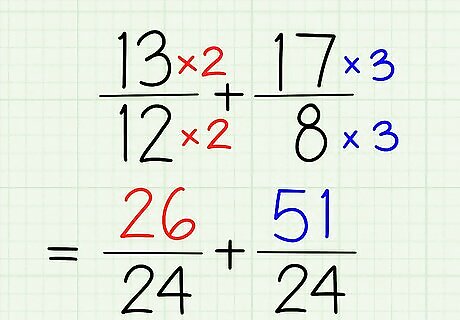
Multiply your numerators and denominators to get your like fraction. Both denominators now need to be turned into 24. How do you get 12 to 24? Multiply it by 2. 8 to 24? Multiply it by three. But don't forget – you need to multiply the numerators, too! So 13 x 2/12 x 2 = 26/24. And 17 x 3/8 x 3 = 51/24. We're well on our way to solving the problem!
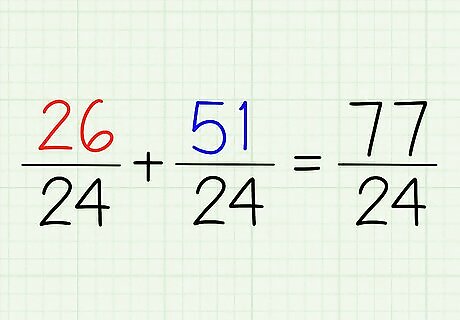
Add or subtract your fractions. Now that you have the same denominator, you can add these two numbers together with ease. Remember, leave the denominator alone! 26/24 + 51/24 = 77/24. There's your one fraction! That top number is mighty big, though....
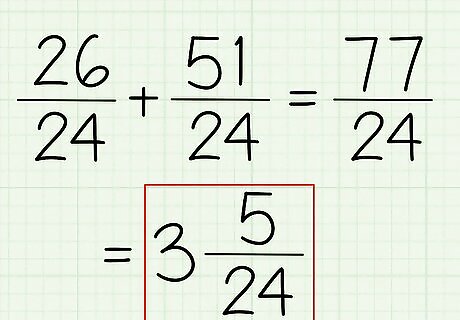
Convert your answer back into a mixed fraction. Having such a large number on top is a little weird – you can't quite tell the size of your fraction. All you have to do is put the denominator into the numerator until in can't be repeated again and then see what you have leftover. For this example, 24 goes into 77 three times. That is, 24 x 3 = 72. But there's 5 leftover! So what's your final answer? 3 5/24. That's it!
Adding and Subtracting Fractions without looking for the LCD
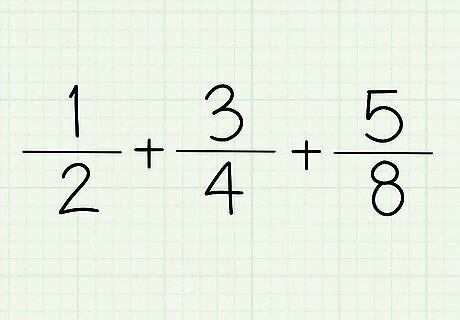
List the fractions. e.g. ½ + ¾ + ⅝
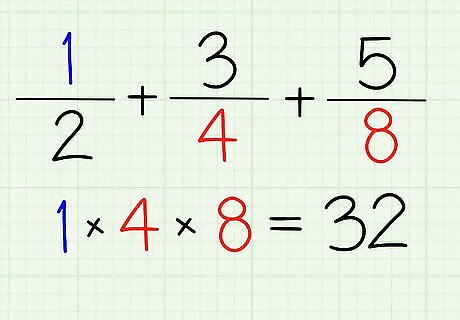
Solve for the numerators first. Multiply ¹ to the denominator/s of the other fractions. Multiply 1 to 4 and 8. [32]
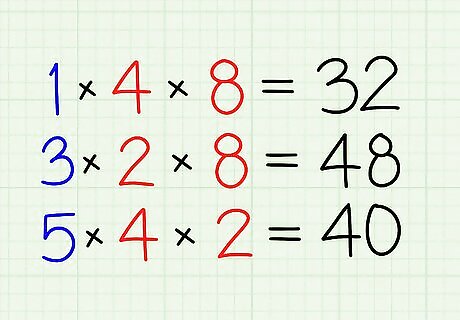
Do as to other fraction. Multiply 3 with 2 and 8. [48] Lastly, multiply 5 with 4 and 2. [40]
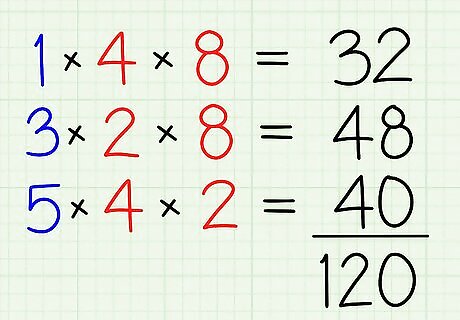
Add all the product. 32+48+40=120
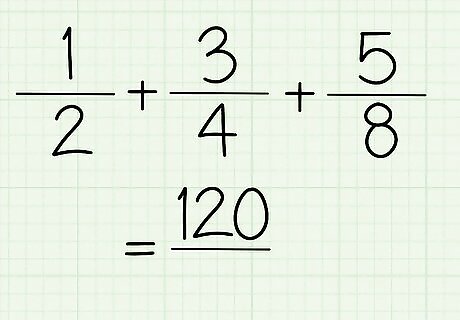
Now you have the numerator.
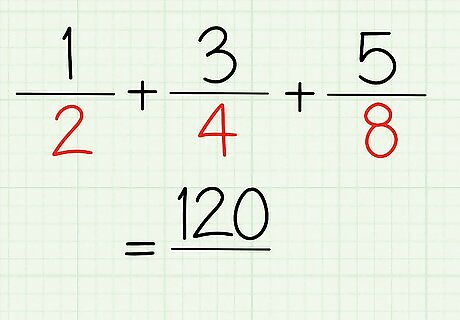
Solve for the denominator.
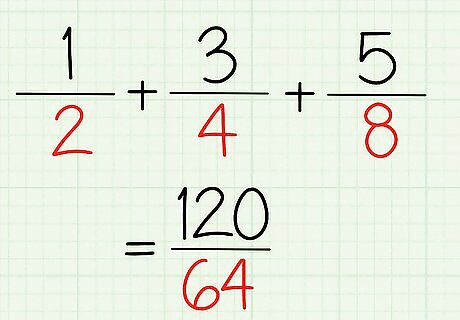
Multiply all the denominator. 2×4×8=64
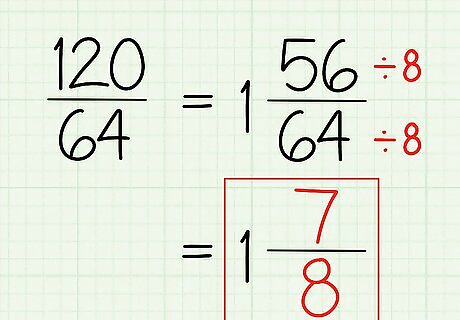
You have the answer. 120/64 = 1 56/64 = 1 ⅞ EXPERT TIP Joseph Meyer Joseph Meyer Math Teacher Joseph Meyer is a High School Math Teacher based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He is an educator at City Charter High School, where he has been teaching for over 7 years. Joseph is also the founder of Sandbox Math, an online learning community dedicated to helping students succeed in Algebra. His site is set apart by its focus on fostering genuine comprehension through step-by-step understanding (instead of just getting the correct final answer), enabling learners to identify and overcome misunderstandings and confidently take on any test they face. He received his MA in Physics from Case Western Reserve University and his BA in Physics from Baldwin Wallace University. Joseph Meyer Joseph Meyer Math Teacher To simplify fractions, you can divide both the numerator and denominator by a common factor. This creates a new, easier-to-use fraction with smaller components, but it represents the same value. For instance, if you divide both the numerator and denominator of 6/12 by 2, you get 3/6, which is equal to 1/2.


















Comments
0 comment