views
Correcting Biceps Imbalances with Exercise
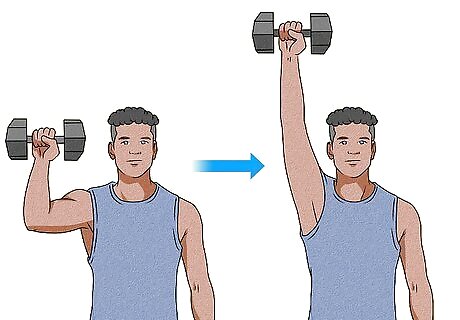
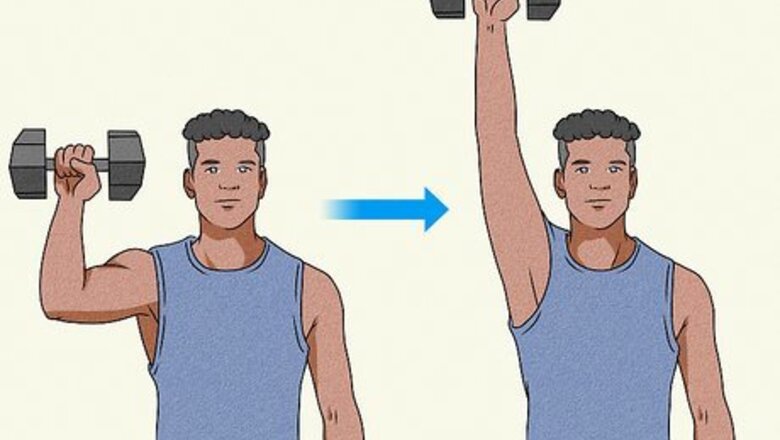
Use unilateral arm exercises to ensure proper balance. When you do bilateral exercises, you may unconsciously shift more weight to the stronger side to compensate. Unilateral training works just one side of your body at a time, which helps ensure that you work both sides equally. Try unilateral isolation exercises that target your biceps, such as: Concentration curls. This is one of the most effective biceps workouts out there! Sit on a chair with a dumbbell in one hand, and let the dumbbell hang down between your legs with your palm facing forward. Keep your wrist straight as you curl the dumbbell toward your shoulder. Slowly return to the starting position. Switch to the other arm after about 20 reps. Hammer curls. Stand with a dumbbell in one hand. Let your hand hang by your side with your palm facing your body. Keeping your arm tucked close to your side, slowly raise the dumbbell to your shoulder and then slowly return to the starting position. Aim for 10 reps on each side. Biceps curl switches. Stand on top of a resistance band with your feet hip-width apart. Grab one handle in each hand with your palms facing forward and your arms close to your sides. Alternate bending your elbows on each side to bring the handle up to your shoulder, then raise the other handle as you return the first to the starting position. Cross-body curls. These are very similar to the curl switches, except that you bring the handle of the resistance band across your torso toward the opposite shoulder. As you lower one hand to the starting position, carefully raise the other.

Start with your weaker arm first. When you’re trying to balance your biceps, let your weaker side set the pace. You’ll want to use the same amount of weight and number of reps on both sides if possible, so starting with the side that needs the most work will help you determine what’s actually feasible for you. For example, if you started with your stronger side, you might be able to breeze through 10 curls with a 15 lb (6.8 kg) weight. But if you can’t manage the same number of reps or the same amount of weight on the other side, you won’t be helping to correct the imbalance! The goal is to eventually close the gap and get rid of the strength difference between your arms. Then, you can go back to doing exercises that are equally challenging for both sides. Avoid doing exercises that use a barbell since you won't properly isolate your weaker arm. Stick with dumbbell exercises until they're balanced out again.
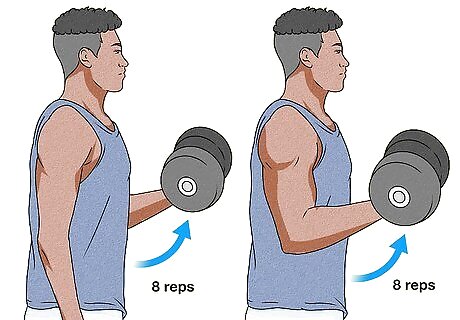
Do the same number of reps on both sides. It might be frustrating to stick to just 8 reps when you know you can knock out 10-15 on your strong side. But if you keep working one arm more than the other, your weaker bicep will never have a chance to catch up! Do as many reps as you comfortably can on your weaker side, then do the same on the stronger side. Over time, you’ll be able to do more reps with your weaker arm. Eventually, it should catch up with your stronger side so that you can move on to doing more on both sides.
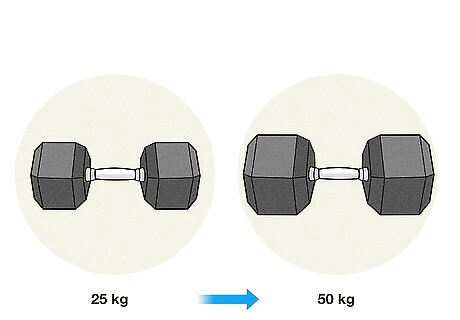
Choose a weight level appropriate for your weaker arm. If possible, you should use the same amount of weight or resistance on both sides. This means you’ll need to start with a weight that’s light enough for your weaker arm to handle. Eventually, you’ll build up enough strength on that side so that you can move up to greater amounts of weight or resistance. For instance, you might start doing curl switches with a light resistance band, even if it feels a little too easy on your stronger side. Once you get comfortable with that, move up to using a medium-weight resistance band.
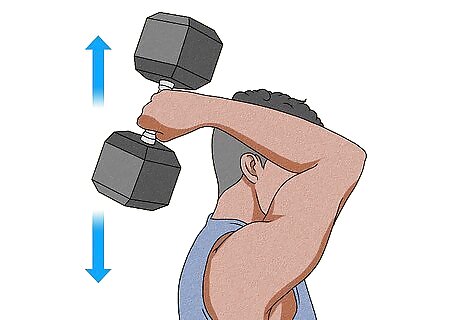
Work out your triceps to avoid muscle pair imbalances. Your biceps and triceps work together as a team to help you flex and extend your arm. If one is weaker than the other, you might be prone to pain, injuries, or a limited range of motion. Do exercises that work your triceps as well as your biceps to keep them in balance. A few great exercises for your triceps include push-ups, body weight chair dips, and overhead resistance band extensions.
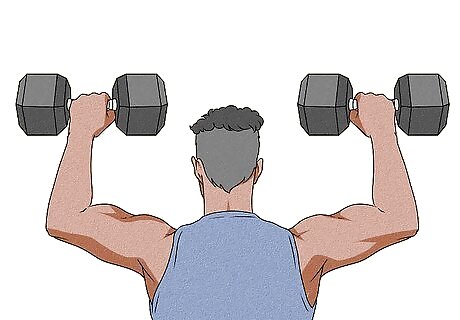
Don’t neglect your bilateral exercises. Unilateral exercises are fantastic for correcting muscle imbalances, but they work best when you pair them with bilateral (2-handed) exercises. Unless your doctor, physical therapist, or trainer recommends otherwise, unilateral exercises should account for about 40% of your strength training routine. Make bilateral exercises the main foundation for your workout. Some good bilateral exercises for your biceps include hammer curls, bent-over rows, seated biceps curls, and seated rows.

Talk to a physical therapist if you have a severe biceps imbalance. Major imbalances can lead to injuries, pain, or loss of flexibility. Or, in some cases, an injury can be the root cause of the imbalance. If you have a severe imbalance or an injury that needs rehabilitation, talk to your doctor. They can refer you to a physical therapist who can help. A physical therapist can evaluate your muscle imbalance, help you identify what might be causing it, and show you exercises that can help correct it.

Make sure you’re using proper form when exercising. Using incorrect or poor form when you exercise can cause imbalances, or make the imbalance you have worse. If you think you might have a biceps imbalance, ask a personal trainer or physical therapist to spot you and make sure you’re doing your arm exercises the right way. If you’re confident enough that you know what you’re looking for, you can also watch yourself in a mirror or have someone take a video of you so you can review your form.
Identifying a Biceps Imbalance
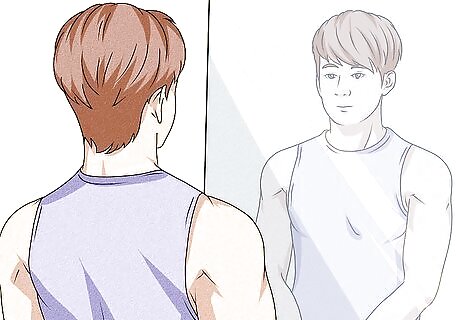
Examine photos or use a mirror to spot obvious imbalances. Sometimes, you might be able to see a visible size difference between your biceps. If you suspect there’s a muscle asymmetry between your biceps, check yourself out in a mirror or ask someone to snap some pictures of you from different angles. Check to see if one arm looks bigger than the other. You can also ask a fitness trainer, workout buddy, or family member to have a look and see if they notice any obvious differences in size. If you suspect there’s a difference between your biceps, but you can’t tell by looking, taking measurements may help. Without flexing, wrap a soft tape measure around the thickest part of your biceps on both arms. Compare the 2 measurements to see if there’s a difference.

Test yourself with unilateral (one-sided) exercises. Doing unilateral exercises, where you perform the exercise with just one side of your body at a time, can help you spot differences in strength. Try a simple test, like seeing if you can comfortably lift the same amount of weight with both arms. For instance, you might try doing a few bicep curls with each arm. Can you easily lift the same amount of weight on each side? Are you able to do the same number of reps on each side? If you can easily lift 20 pounds (9.1 kg) with your right hand, but not with your left, then you probably have a muscle imbalance.
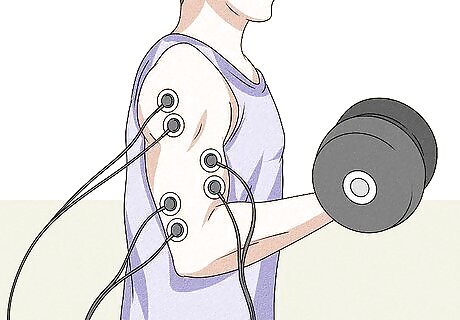
Get biometric muscle testing to identify hard-to-spot imbalances. You can get a more exact idea of how imbalanced your muscles are with evaluation from a doctor or physical therapist. If you’re concerned about a possible imbalance, give your doctor a call. Explain that you’d like to have testing done to measure the relative strength of your biceps on both sides. Your doctor or physical therapist may hook you up to a machine that measures the strength and endurance of your muscles while you do exercises or other activities. They can compare the results and identify any imbalances between your biceps.

Look for a limited range of motion to spot a pair imbalance with your triceps. When you think of a biceps imbalance, you might imagine having one arm that’s weaker than the other. However, it’s also possible to have an imbalance between different muscles in the same arm. If you have trouble flexing or extending your arm completely, ask your doctor if you may have an imbalance between your biceps and triceps. Many muscle groups work together to help you move your body, so you need to focus on all the muscles in the group in order to prevent imbalances. This type of muscle imbalance can make you more prone to injuries, so it’s important to work on correcting it.


















Comments
0 comment