views
Germinating Seeds Naturally
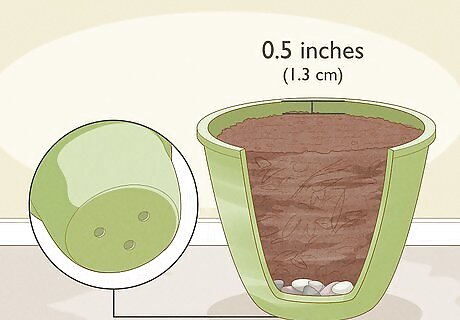
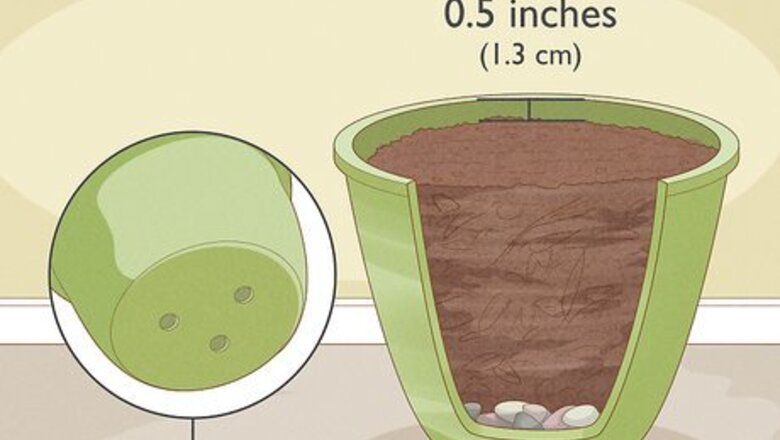
Add stones and natural compost to a plant pot. Begin the planting process during autumn. Get a medium-sized plant pot that has drainage holes at the bottom. Layer the bottom of the pot with small stones. Only put enough stones so that you can’t see the bottom of the pot. Then, fill the pot with natural compost. Fill it up almost all the way, but leave about a 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) of space at the top of the pot. Natural compost is made out of decomposing organic materials, such as leaves, hay, and raw vegetables. You can use store-bought compost if you do not have homemade compost.

Plant the seeds. Once the pot has been filled with compost, dig out a small hole in the center of the pot. It should be about 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) deep. Insert 2 or 3 seeds into the hole. Then, replace the compost and pat it down. After that, water the compost until it appears wet.

Put the pot in a shady spot. You can put the pot outside in a shady corner, or you can put it near a window that doesn’t get much light. Wherever you put it, the spot should not receive constant sunlight. Keeping the seeds at a temperature between 65 °F (18 °C) and 75 °F (24 °C).
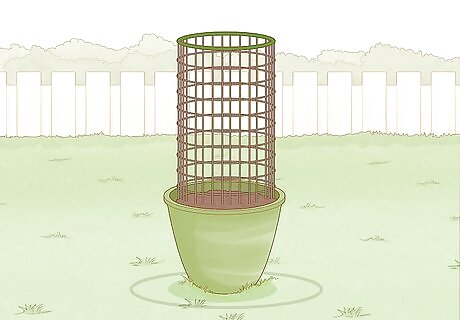
Protect the seeds with wire mesh if your pot is outside. This will prevent birds and animals from eating the seeds. First figure out the circumference of the top of the pot. Use wire cutters to cut the wire mesh a little larger than the measurement you took. Then, put the wire mesh on top of the pot and fold the wire mesh over the edges. Make sure that it is secure and can’t be easily removed.
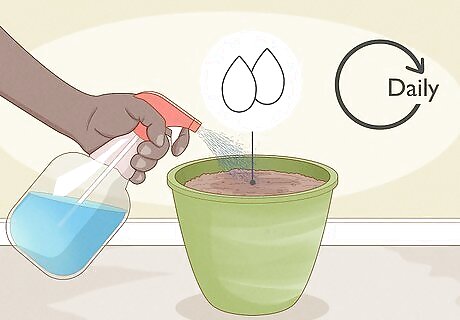
Keep the soil damp. Check the soil daily to see if it is dry. If it is, add water to the soil. The soil should be damp but not wet.

Check the seeds for growth. Natural germination will take longer than assisted germination. Your seeds will likely take 2 seasons to complete the germination process. If you planted the seeds in early autumn, check their progress in early spring. They have completed germinating if you see a small sprout growing out of each seeds.
Using Assisted Germination

Use hot water to stimulate a “fake” summer. To speed along the process of germination, you can trick the seeds into “thinking” they’ve gone through the typical dormancy and germination period. A seed may take 2 seasons to germinate naturally, but this process will speed up germination to 90 days. To begin, gather your materials to replicate the summer season. You will need: A container that can hold hot water and all of your seeds Your seeds Warm or hot (not boiling) water

Place the collected seeds in your container. Then, pour the hot water over them. Make sure the seeds have been completely covered with water. At this stage, it doesn't matter whether they sink or float.

Wait 24 to 48 hours to dispose of any floating seeds. Floating seeds typically mean that they are empty and will not produce a seedling. You may replace the water after 24 hours with more warm water, and wait another day if you want to give them another chance to float.
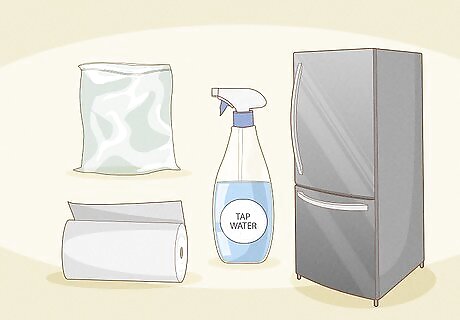
Use your refrigerator to replicate a “fake” winter. After you’ve replicated the summer season, it is time to replicate cold weather. Prepare the following materials before you proceed: A plastic sandwich bag Paper towel Tap water Refrigerator

Place your seeds on the paper towel. Fold the paper towel and moisten it with water so it is wet, but not dripping. Then, insert the paper towel into the plastic sandwich bag. Make sure that the seeds don’t fall out.
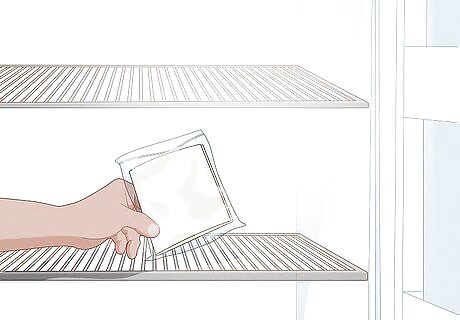
Place the plastic sandwich bag in your refrigerator. This process is called cold stratification. Put the sandwich bag in a place where it won’t be bothered. Typically, the bottom drawer is a good spot for the sandwich bag. It’s a good idea to label the bag with something like “tree seeds” to avoid disturbance. Don’t put the seeds into the bottom drawer if it is on a humidity control setting.
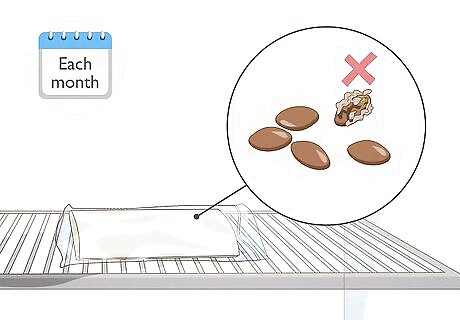
Check for rotten seeds each month. To check, open the bag without letting the seeds fall out. Look at the seeds. They should be larger, but should not appear spongy. If they appear engorged and spongy, take them out of the bag. Throw them out if they feel spongy.
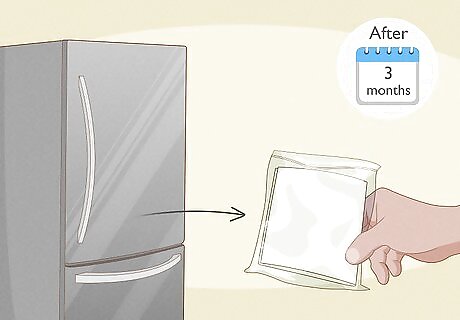
Take your seeds out of the refrigerator after three months. If you’ve left the seeds in the refrigerator, the cold stratification will be completed after 90 days. Remove them from the refrigerator to begin the final stage of the assisted germination process.
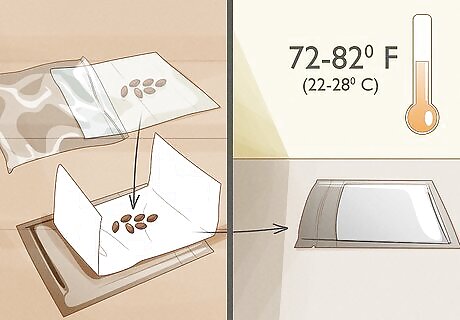
Put the seeds in another bag. Put the seeds in a paper towel and fold it. Then, put the paper towel in a plastic bag. Place the plastic bag in a warm location. 72 to 82 °F (22 to 28 °C) is an ideal temperature for the seeds. Once the seeds begin to sprout, it is time to pot or plant them. The time it will take them to sprout depends on the type of seeds you have. Check the progress of the seeds once a week.
Planting the Seedlings
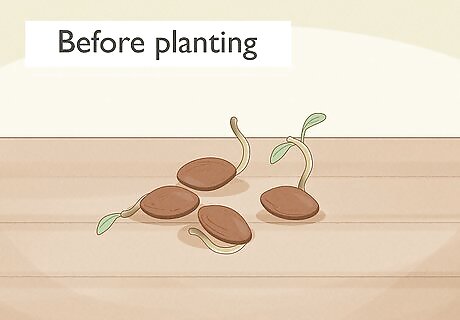
Make sure the seeds have germinated before planting. The seeds should have produced sprouts before repotting them or planting them. And to sprout, the seeds need to go through the process of germination. You can use natural or assisted germination to complete the process.

Repot or plant the seedlings in the spring. Seedlings should begin to appear around springtime. If they have grown significantly, you can repot them or plant them outside. Keep in mind that seedlings are often targeted by weeds and animals, so it is typically better to protect them inside for about a year. Use a potting soil that release nutrients slowly.
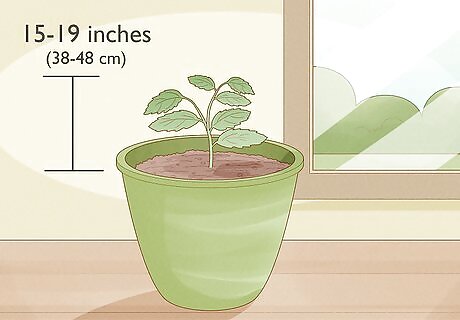
Nurse the seedlings indoors until they are 15 to 19 inches (38 to 48 cm) tall. If you choose to protect the seedlings until they grow larger, keep the seedlings inside in a sunny area. Keep the seedling inside for about a year, until they reach 15 to 19 inches (38 to 48 cm) tall. Keep the soil damp during this time. You may need to water the soil daily if it does not stay damp.
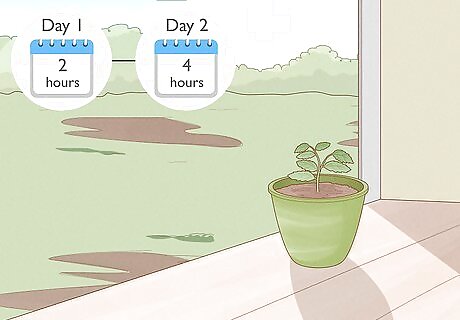
Expose the seedlings gradually to the outside. Because the seedlings have mostly or only grown indoors, slowly begin to expose them to the outside after a year. The best time to begin exposure is during early spring. Ideally, put the pot in a place with dappled sunlight. Start by putting the seedlings outside for 2 hours during the day. Then, increase the daily outside time by an hour each day. After a few days, permanently move the seedlings outside.
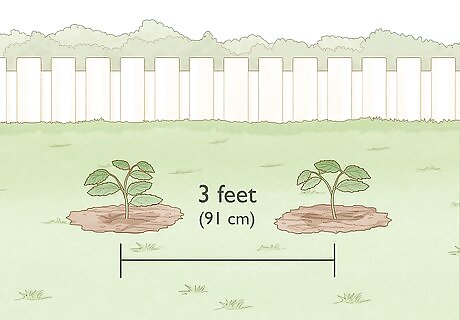
Plant the seedlings. If the tree won’t grow very large, it’s okay to keep it in a pot. For most trees, it will be necessary to plant them in the ground. Find a clear location with plenty of sunlight. Dig a hole that is at least an inch deep, depending on the size of the seedlings. Plant the seedlings and cover the hole back up with soil. Plant the seedlings at least 3 feet (91 cm) apart if you are planting multiple trees. Rake the area so that it is clear before planting the seedlings.
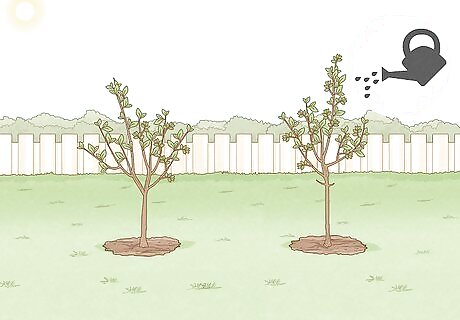
Watch the progress of your trees. Trees take years to grow, and they will continue to grow in some way or another throughout their lifespans. Watch your tree carefully while it is a sapling. Keep it watered, and protect it from animals if necessary. You can put a mesh fence around the tree to protect it.
















Comments
0 comment