views
- Multiple versions of Python (e.g., Python 2 and Python 3) can be installed on the same system.
- Use "python --version" to check the system version of Python.
- Use "python3 --version" to check the version of Python 3, and python2 --version to check the version of Python 2 individually.
Checking on a Mac
Open a Terminal window. To do so, just open the Launchpad, type terminal, and click Terminal in the search results.
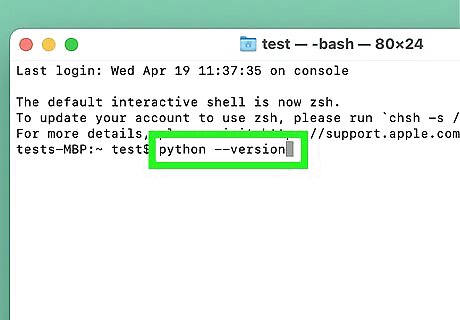
Type python --version and press ⏎ Return. This displays the version of Python installed on your computer. If you have Python 3 in addition to Python 2.7 (the version that used to come preinstalled on macOS), you can check the Python versions separately: Check the Python 2 version: python2 --version Check the Python 3 version: python3 --version You can also use the whereis python command to see where Python is installed.
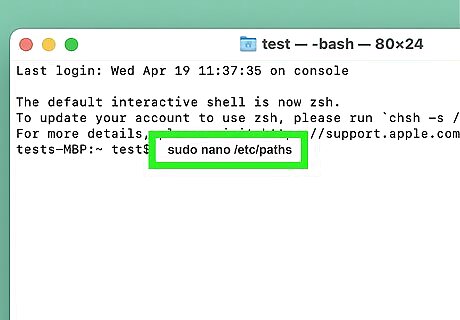
If Python is not found, add the path. If you've installed Python but see "command not found" or similar when trying to check the version, you'll just need to add the Python path variable. Type sudo nano /etc/paths and press Return. On the last line of the file, add the full path to Python. This is usually /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework. Save the file by pressing Ctrl + O and then Ctrl + X. Close the Terminal and open a new one. Now, when you type python --version, you'll see the Python version.
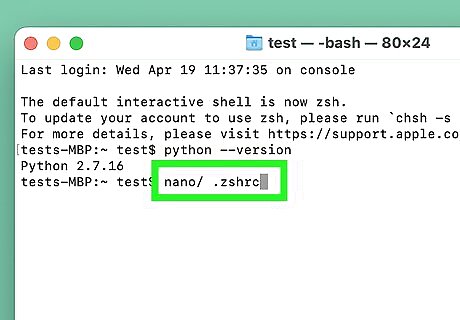
Change the default python to Python 3 (optional). If you have multiple Python versions installed and want to change the system version to Python 3, it's easy. You'll just need to edit your .zshrc or .bashrc file to create an alias. Here's how: In a Terminal, type nano ~/.zshrc and press Return. If the file does not already exist, use nano ~/.bashrc instead. Paste this line at the bottom of the file: alias python=/usr/local/bin/python3. Save the file by pressing Ctrl + O and then Ctrl + X. Close the Terminal and open a new one. Now, when you type python --version, you'll see the Python 3 version. EXPERT TIP Kevin Burnett Kevin Burnett Software Developer Kevin Burnett is a Software Developer with over 20 years of professional experience. He spent the majority of his career at Rosetta Stone, a language-learning software company. He has experience with both front and back-end development and works primarily in Ruby, Python, and JavaScript. Kevin Burnett Kevin Burnett Software Developer Commands check versions. Don't overcomplicate checking your Python version — just run "python --version" in terminal! This quick command invokes interpreter flags to instantly output the current installed production release.
Checking on Windows
Open PowerShell. You can do this quickly by pressing Windows key + S, typing powershell, and clicking Windows PowerShell. You can also right-click the Start menu and select PowerShell or Terminal (if either are present). This command to check your Python version will work the same no matter which option you choose.
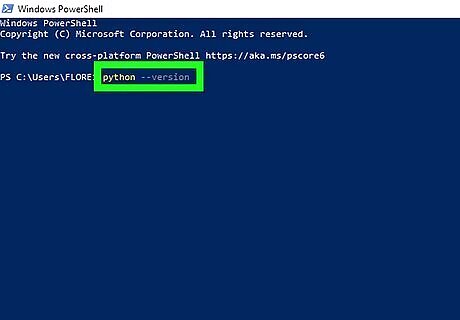
Type python --version and press ↵ Enter. If Python is installed, this command will display the version number of your primary version of Python. If you have multiple versions of Python installed, you can check each version individually. Check the Python 2 version: python2 --version Check the Python 3 version: python3 --version You can also use the command get-command python* to see all installed versions of Python and their paths.
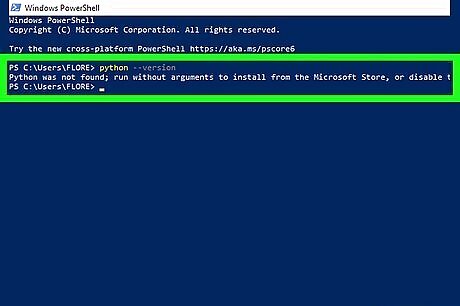
If Python is not found, add the path to your environment variables. If you're sure you've installed Python but see a "Python not found" when checking the version, there's an easy fix: In File Explorer, find the folder in which Python is installed. It's usually something like C:\Users\yourname\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311. In the Windows Search bar, type sysdm.cpl and press Enter. Click Environment Variables… Under "User Variables," select the Path variable and click Edit. If the path to Python does not appear, click New, paste the full path (e.g., C:\Users\yourname\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311, and press Enter. Click New again, and paste the path to the scripts directory. It's the same path, but with \Scripts at the end, e.g., C:\Users\yourname\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Scripts. Click OK until you've exited out of the app. Close your PowerShell window and open a new one. You should now be able to check the version with python --version.
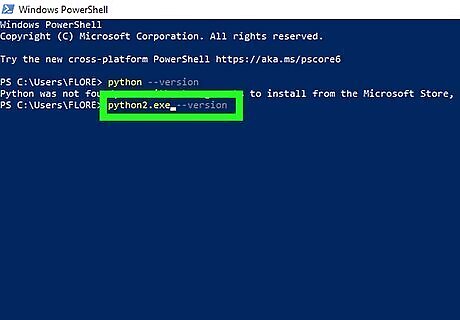
Use multiple versions of Python at once (optional). If you had Python 2 installed before installing Python 3, python.exe will always start Python 2 instead of Python 3. Just use python3 when you want to use Python 3, and python when you want to use Python 2. Alternatively, you can rename the python.exe file in your Python 2 directory to python2.exe, and just use python2 when you want to use the Python 2 interpreter. When you installed Python 3, the installer also created a file called python.exe in your Python 3 install directory. This means that once you rename the Python 2 version of python.exe, typing python should automatically launch Python 3 as long as your Python 3 installation path is correct. Double-check your Python 3 installation path to make sure you have a file called python.exe there. If not, copy python3.exe and rename the copy python.exe for the same effect.
Checking on Linux
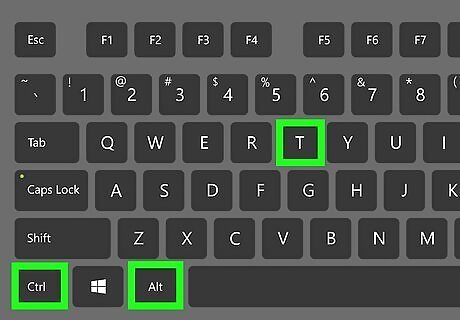
Open a Terminal window. If you're using Linux, you can usually open a Terminal by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T at the same time.
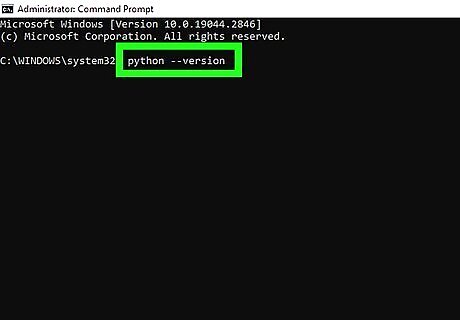
Type python --version and press ⏎ Return. This displays the system version of Python installed on your computer. If you have Python 3 in addition to Python 2.7 (the version that used to come preinstalled on macOS), you can check the Python versions separately: Check the Python 2 version: python2 --version Check the Python 3 version: python3 --version You can also use the whereis python command to see where Python is installed. If you want to check the installation directory of Python 3 specifically, use whereis python3 instead.
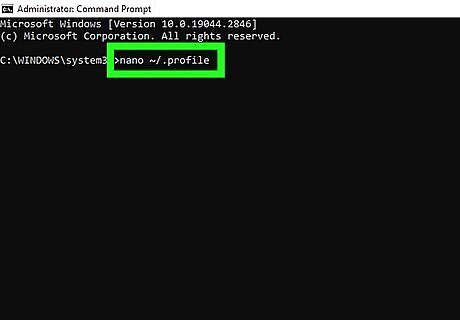
If Python is not found, add the path. If you've installed Python but see "command not found" or similar when trying to check the version, you'll just need to add the Python path variable. Type nano ~/.profile and press Enter. Add the path to the version of Python you've installed to the last line of the file like this: PYTHONPATH=/usr/bin/python. Save the file by pressing Ctrl + O and then Ctrl + X. Close your Terminal, then open a new one. Type python --version to see the Python version.
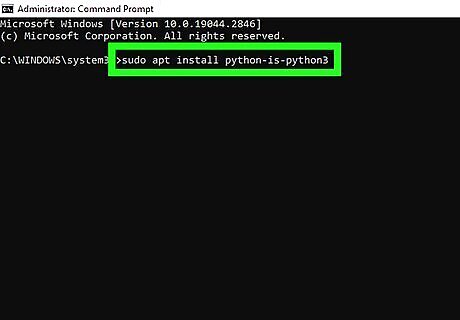
Change the default python to Python 3 (optional). If you want to use Python 2 and Python 3 at the same time and want to make the python command launch python3, you have a few options:
On Ubuntu and Linux Mint, install python-is-python3 using the command sudo apt install python-is-python3. This ensures that running the python command always uses the Python 3 interpreter instead of other installed versions.
On other versions (or if you don't want to install a package), just create a symbolic link that makes the python command start python3 instead:
Use ls -l /usr/bin/python* to see all symbolic links for python. If /usr/bin/python is linking to anything other than your preferred version, you can change the link.
To change the link, use the command sudo ln -fs /usr/bin/python
Installing Python
Windows. If you see "Python was not found" when checking the version, see our Python installation guide for Windows, or install using one of these two simple options: Download the latest version of Python from https://www.python.org/downloads. Once downloaded, double-click the installer, and follow the on-screen instructions to install. When installing, make sure to choose the option to add Python to your path. You can also install Python from the Microsoft Store. Just open the Microsoft Store app on your Windows 10 or 11 PC and search for python. Click the latest version of Python (e.g., Python 3.11), click Get, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Mac. If Python isn't installed on your Mac, there are two easy ways to install it: You can download the latest Python installer from https://www.python.org/downloads. Once downloaded, double-click the .pkg file and follow the on-screen instructions. Alternatively, you can use Homebrew: In a Terminal window, type xcode-select --install and press Return. This installs Xcode, Apple's developer tools. Type or paste this command to install Homebrew: ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)". Once you press Return, Homebrew will install. Type brew install python3 and press Return to install Python3.
Linux. The best way to install Python on Linux is to use your distribution's repositories. First, you'll want to find out which version of Python you need: Using Apt on Ubuntu and Linux Mint: Type sudo apt update and press Enter. Type sudo apt install python3 and press Enter. Arch Linux: Type packman -S python and press Enter. Fedora, Red Hat, & CentOS: Type sudo yum -y update and press Enter. Type sudo dnf install python3 and press Enter.

















Comments
0 comment