
views
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) can seem daunting, but it holds a key benefit: reducing your tax burden. One way to achieve this is by claiming deductions available under various sections of the Income Tax Act. These deductions allow you to subtract certain expenses from your taxable income, lowering the total amount taxed by the government. Let’s explore various deductions to save on your taxes.
Also Read: Income Tax Return Filing: 10 Mistakes To Avoid When Filing ITR For AY 2024-25
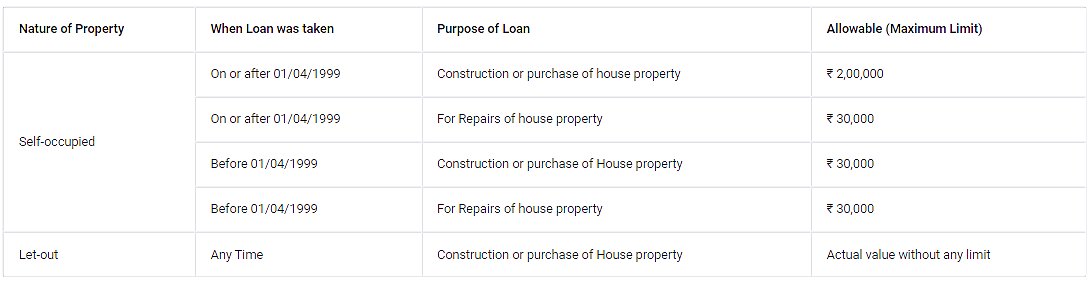
Section 24(b)
Deduction from Income from house property on interest paid on housing and housing improvement loans. In the case of self-occupied property, the upper limit for deduction of interest paid on a housing loan is Rs 2 lakh. However, this deduction is not available for people opting for the new tax Regime.
Interest on loan u/s 24(b) allowable is tabulated below:
Tax deductions specified under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act
These deductions will not be available to a taxpayer opting for the new tax regime u/s 115 BAC, except for deduction u/s 80CCD(2) which will be allowable under the new tax regime as well.
80C, 80CCC, 80CCD (1)
Deduction towards payments made to
80C
A combined deduction limit of Rs 1,50,000
- Life Insurance Premium
- Provident Fund
- Subscription to certain equity shares
- Tuition Fees
- National Savings Certificate
- Housing Loan Principal
- Other various items
80CCC
Annuity plan of LIC or other insurer towards pension scheme
80CCD (1)
Pension scheme of the central government
80CCD (1B)
Deduction Limit of Rs 50,000
Deduction towards payments made to the pension scheme of the central government, excluding deduction claimed under 80CCD (1).
80CCD (2)
Deduction towards contribution made by an employer to the pension scheme of the central government- Deduction limit of 10% of salary
If the employer is the central government- A deduction limit of 14% of the salary
80D
Deduction towards payments made to health insurance premium & preventive health check-up
For self/spouse or dependent children
- Rs 50,000 if any person is a senior citizen
- Rs 5,000 for preventive health check up, included in above limit
For Parents
- Rs 50,000 if any person is a senior citizen
- Rs 5,000 for preventive health check up, included in above limit
Deduction towards medical expenditure incurred on a senior citizen, if no premium is paid on health insurance coverage
For self/spouse or dependent children- The deduction limit is Rs 50,000
For parents- The deduction limit is Rs 50,000
80DD
Deduction towards payments made towards maintenance or medical treatment of a disabled dependent or paid/deposited any amount under the relevant approved scheme.
- A flat deduction of Rs 75,000 is available for a person with a disability, irrespective of the expense incurred
- The deduction is Rs 1,25,000 if the person has severe disability (80% or more)
If the taxpayer is claiming deduction u/s 80DD then it’s recommended to file form 10-IA also before filing of return. Form 10IA can be filed later also however it is recommended to file form 10-IA along with the return of income to avoid any inconvenience later.
80DDB
Deduction towards payments made towards medical treatment of self or dependant for specified disease- Deduction limit of Rs 40,000
(Rs 1,00,000 if senior citizen)
80E
Deduction towards interest payments made on loan for higher education of self or relative- Total amount paid towards interest on loan taken
80EE
Deduction towards interest payments made on loan taken for acquisition of residential house property where the loan is sanctioned between April 01, 2016 to March 31, 2017- Deduction limit of Rs 50,000 on the interest paid on loan taken
80EEA
Deduction towards interest payments made on loan taken for acquisition of residential house property for the first time where the loan is sanctioned between April 01, 2019 to March 31, 2022 and deduction should not have been claimed u/s 80EE- Deduction limit of Rs 1,50,000 on the interest paid on loan taken
80EEB
Deduction towards interest payments made on loan for the purchase of electric vehicle where the loan is sanctioned between April 01, 2019 to March 31, 2023- Deduction limit of Rs 1,50,000 on the interest paid on loan taken
80G
Deduction towards donations made to certain funds, charitable institutions, etc.
Donations are eligible for deduction under the below categories:
Without any limit
- 100% deduction
- 50% deduction
Subject to qualifying limit
- 100% deduction
- 50% deduction
80GG
Deduction towards rent paid for house & applicable only for whom HRA is not part of the salary.
Least of the following shall be allowed as deduction:
Rent paid reduced by 10% of total income before this deduction- Rs 5,000 per month- 25% of Total Income before this deduction
Form 10BA to be filed for claiming this deduction
80GGA
Deduction towards donations made for scientific research or rural developmentDonation are eligible for deduction under the below categories:
Research association or university, college or other institution for
- Scientific research
- Social science or statistical research
Association or institution for
- Rural development
- Conservation of natural resources or for afforestation
PSU or local authority or an association or institution approved by the national committee for carrying out any eligible project
Funds notified by the central government for
- Afforestation
- Rural development
National urban poverty eradication fund as setup and notified by central government
No deduction shall be allowed under this section in respect of donations made in cash exceeding Rs 2000/- or if gross total income includes Income from profit/gains from business/profession
80GGC
Deduction towards donations made to political party or electoral trust- Deduction of total amount paid through any mode other than cash
80TTB
Deduction on interest received on deposits by resident senior citizens- Deduction limit of Rs 50,000
80U
Deductions for an individual taxpayer with disability
- Flat Rs 75,000 deduction for a person with disability, irrespective of expense incurred
- Flat Rs 1,25,000 deduction for a person with severe disability (80% or more), irrespective of expense incurred
In addition to tax benefits applicable regardless of age of taxpayer, there are certain enhanced / additional benefits for senior/super senior citizen. The additional benefits are listed below:
Paper filing of Income Tax Return
Super senior citizens (aged 80 years or more) have the option to submit their ITR using Form 1 or 4 in offline/paper mode. The e-filing option also remains available to them.
Relief from payment of Advance Tax
As per Section 208, every person whose estimated tax liability for the year is Rs 10,000 or more, shall pay his tax in advance, in the form of advance tax. But, Section 207 gives relief from payment of advance tax to a resident senior citizen. Thus, a resident senior citizen, not having any income from business or profession, is not liable to pay advance tax.
Income tax deduction on interest on bank deposits
Section 80TTB of the Income Tax Act allows tax benefits on interest earned from deposits with banks, post offices or cooperative banks. The deduction is allowed for a maximum interest income of up to Rs 50,000 earned by the senior citizen. Both the interest earned on saving deposits and fixed deposits are eligible for deduction under this provision.
Also, u/s 194A of the Income Tax Act, no tax is deducted at source (TDS) on interest payment of up to Rs 50,000 by the bank, post office or co-operative bank to a senior citizen. This limit is to be computed for every bank individually.
Tax benefits to medical insurance and expenditure
According to Section 80D of the Income Tax Act, senior citizens may avail a higher deduction of up to Rs 50,000 for payment of premium towards medical insurance policy. The limit is Rs 25,000 in case of non-senior citizens.
Further Section 80DDB of the Income Tax Act allows tax deduction on expenses incurred by an individual on himself or a dependent towards the treatment of specific diseases as stated in the act. The maximum deduction amount in case of a senior citizen is Rs 1 lakh (Rs 40,000 for non-senior citizen taxpayers).



















Comments
0 comment