views
Spotting Early Signs of a Pulled Trapezius
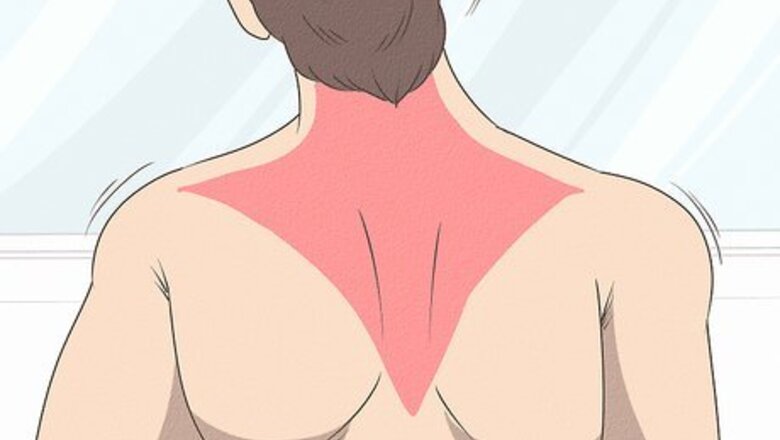
Pay attention to any difficulty you have moving your head or shoulders. The job of the trapezius is to support your head. When you injure your trapezius by pulling it, its going to have a harder time doing its job. Because of this, you might find that you have a hard time moving your head, neck and shoulders like you normally do.
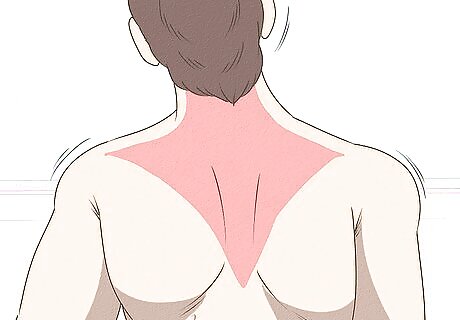
Monitor any loss of strength you have in one or both of your arms. Aside from being the workhorse that keeps your head up, your trapezius is also connected to your arms. When your trapezius gets injured, one or both or your arms might become weak, as if there is nothing supporting it (or them).
Note any muscles spasms or stiffness that you feel. When the muscle fibers in the trapezius get stretched too far, or get torn, the muscle fibers also contract at the same time and become tight. When this happens, it can create a of block of sorts that doesn't allow enough blood to get to the area. This lack of blood can cause your muscles to spasm (it will feel like your muscle is twitching under your skin) or stiffness (which will feel like your muscles have turned to cement).
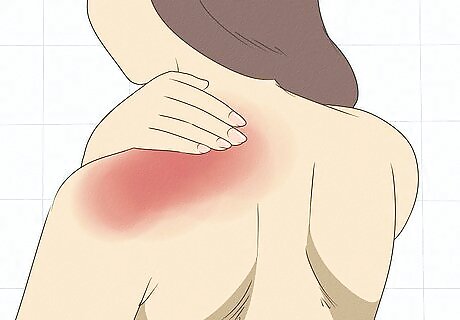
Watch out for pain in your neck and shoulders. As mentioned above, when the muscle fibers in the trapezius constrict, they let less blood into the area, which also means the area gets less oxygen. Oxygen helps break up lactic acid, so when there is not enough oxygen, the lactic acid builds up and creates pain. The pain can be described as sharp pain, a stinging sensation, or feeling like your muscle has been tied into knots.
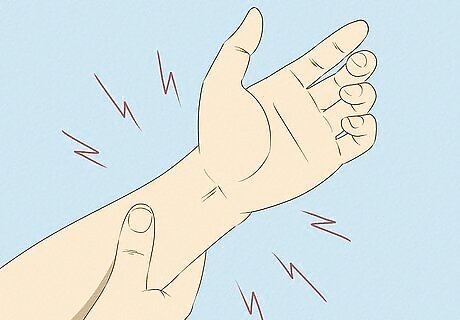
Pay attention to any tingling sensation you feel in your arms. On top of the muscle spasms and pain caused by insufficient blood flow, not having enough blood in the area also causes a strange tingling sensation that you will most likely feel in your arms. This happens because the muscle fibers in the area are constricted.
Spotting Late Signs of a Pulled Trapezius

Keep track of any fatigue you feel. Depending on your pain tolerance, you might feel more or less tired than other people suffering from the same injury. This is because when your body is in pain, your mind goes into overtime trying to find a way to control the pain. This can make you feel really tired and like you have very little energy. Someone with a high pain tolerance might feel a normal amount of energy, but this does not mean that they are any less injured than someone who is extremely fatigued.

Know that a pulled trapezius can reduce your ability to concentrate. Like feelings of being super tired, pain can also affect your ability to concentrate. While the pain is not actually making your ability to concentrate any weaker, your mind might be so busy dealing with the pain that you psychologically feel like you can't focus on anything. Even when you try to focus on something, the pain you are experiencing might distract. Its the same thing that happens when someone tells you not to think about an elephant and then all you can think about is an elephant.
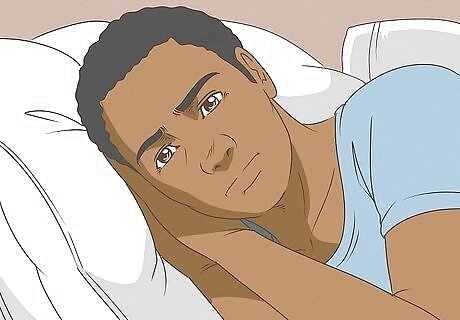
Look out for any sleeplessness you experience. The pain you feel from the pulled trapezius might keep you up at night. In this instance, its not your brain trying to keep you from thinking about the pain, but the actual pain itself that is keeping you up. You might find that every time you try to roll over you feel a sharp pain in your back or head.
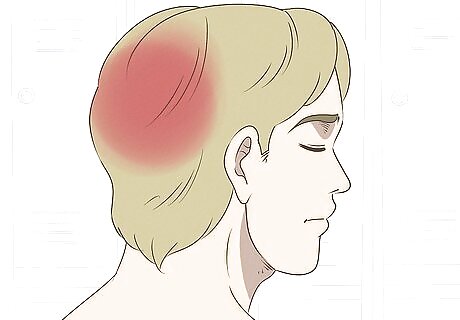
Monitor any headache you feel at the back of your head. Trapezius muscles are connected to the neck muscles and to dura matter (a thin tissue that is pain- sensitive and covers the brain). Any damage to the trapezius muscles can cause headaches because the pain can be easily felt by the dura matter and the brain can interpret pain easily.
Healing Your Trapezius
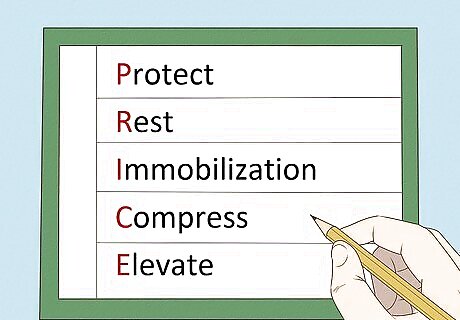
Follow the PRICE therapy technique. This is one of the best ways to get your trapezius on the road to recovery. The PRICE therapy is actually a series of things that you should do. The following steps will go into the details of each part of the therapy.They include: Protect. Rest. Immobilization. Compress. Elevate.
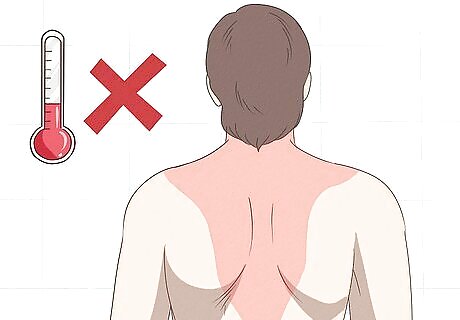
Protect your trapezius. If your trapezius gets hurt more than it already is, it could lead to an even more serious injury, such as a tear. To keep this from happening, you need to protect your pulled muscle. In order to protect your muscle, avoid the following: Heat: Avoid hot baths, heat packs, saunas or any hot environment as heat causes blood vessels to dilate (open up), therefore increasing the risk of bleeding, as more blood will flow to dilated blood vessels. Further movement: Any excessive movement of the affected area may cause further injury. Massage: Pressure to the affected area may contribute to further injury.
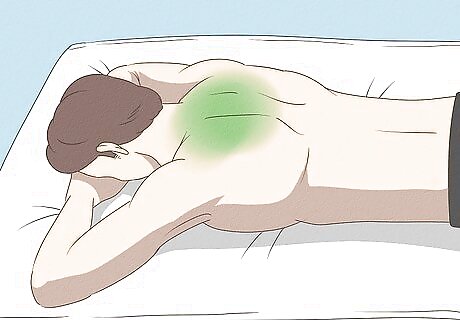
Give your pulled trapezius plenty of rest. You should avoid any activity that may cause further injury to your pulled muscle for at least 24 to 72 hours. As it is, the pain you feel will probably automatically keep you from doing anything crazy, but a reminder never hurt. Rest helps promote the healing process without causing further damage to your injured muscle.
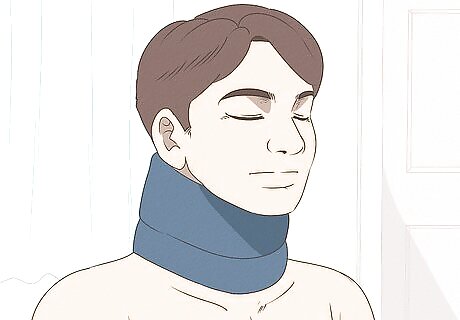
Immobilize your trapezius. As mentioned above, its generally best to give your muscle a rest when it gets injured. Normally a hurt muscle, like a calf muscle, can be wrapped against a splint to keep it immobilize. The trapezius is a bit harder to wrap. In fact, normally you won't wrap your trap, but your doctor might recommend that you wear a soft neck brace to immobilize your neck and keep it from doing further damage to your trap.
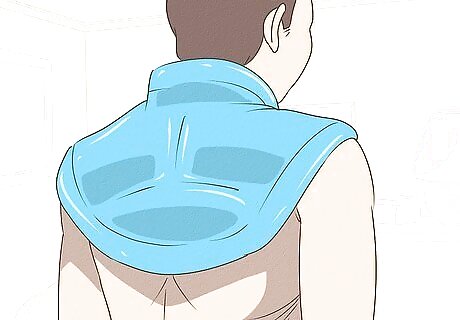
Compress your trapezius with ice. Put an ice pack or a bag of ice on your neck and shoulders to keep the swelling down and the pain you feel to a minimum. The ice will stimulating the flow of lymph fluid, which carries important nutrients to the damaged tissues surrounding the injury. Lymph fluid also removes waste from cells and body tissues which is an important function during the tissue regeneration process. You should place your ice pack or back of ice on your trapezius for 20 minutes at a time. Wait two hours and then put the ice pack back in place. You should repeat this process four to five times each day during the first days (24 to 72 hours) of your muscle injury.
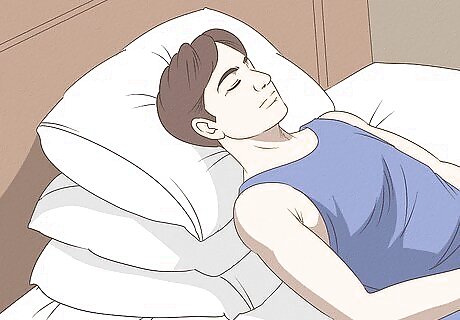
Elevate your muscle. Make sure that the affected area is always elevated. In trapezius muscle injuries, you will want to keep your back and shoulders slightly upright when you sleep. Try putting several pillows behind you so that you are propped up at a 30 to 45 degree angle. Doing this promotes good blood circulation to the injured area and speeds up the healing process.
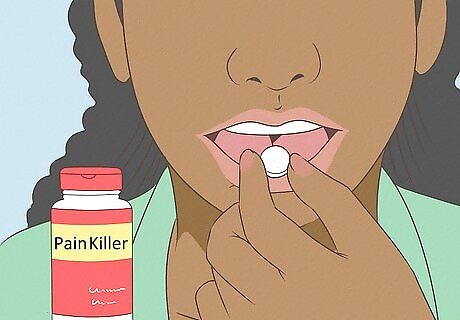
Take painkillers. Painkillers work by blocking and interfering with the pain signals going through the brain. If the pain signal does not reach the brain, then pain cannot be interpreted and felt. Pain killers are classified as: Simple Painkillers: These can be bought over-the-counter (OTC) at a pharmacy and includes Paracetamol. Stronger Painkillers: These are taken when pain is not relieved by OTC painkillers. These can only be prescribed by a doctor and include codeine and tramadol.
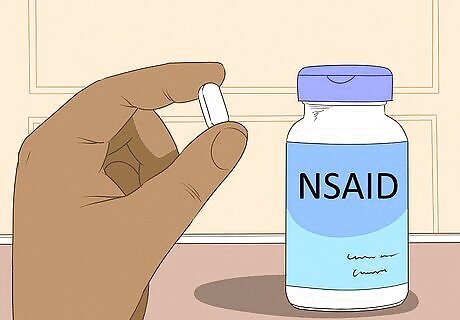
Try some NSAIDs. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) work by blocking specific body chemicals that cause your pulled muscle to become inflamed. causes the affected area to get inflamed.. However, NSAIDs should not be taken in the first 48 hours of injury as they can delay healing. In the first 48 hours, inflammation is one of the ways your body deals with the injury. Examples are Ibuprofen, Naproxen and Aspirin.
Strengthening Your Trapezius

Enlist the help of a physical therapist. For help strengthening the upper trapezius muscle and maintaining its optimal function, you may be referred to a physical therapist. Specific exercises aids in preventing upper trapezius pain. The following exercises may be performed with 15 to 20 reps every hour during the day. Scapular Pinches. You will be instructed to move your shoulders back in a circular motion, and then pinch shoulder blades together. Shoulder Shrugs. It is done by raising the shoulders up until it reaches the ears and then lower it back. Neck Rotation. Rotate the head to the right first, and then repeat on the opposite side.

Strengthen your trapezius with exercises at home once it has healed. Once your trapezius feels like it has returned to normal, you should begin some gentle exercises to make sure that it does not get injured again. There are several exercises you can do to strengthen your trap. You may want to consult a physical therapist or muscle specialist again before doing this exercises if you are not sure that your muscle is fully healed. Try shoulder touches. Stand straight with your shoulders relaxed. Slowly look forward and then move your head so that your ear moves toward your shoulder. Your ear should be as close to your shoulder as possible without it hurting or feeling like you are straining it too hard. Hold this position for 10 seconds and then do the same thing on the other side of your body. Try chest touches. Stand straight with your shoulders relaxed. Slowly tilt your head so that your chin goes towards your chest. Make sure that your shoulders stay down and rested while you do this. Hold this position for 10 seconds. Do this exercise two or three times a day.
Talk to your doctor or physical therapist about surgery if this injury continues to occur. If your have very severely pulled or torn your trap, you may need to get surgery, particularly if it doesn't seem to grow stronger, even when you try to strengthen it with exercises. However, this is only considered when all of the other methods have failed. The surgery repairs and reconnects the damaged trapezius muscle tissue to help it regain its function.


















Comments
0 comment