views
X
Trustworthy Source
National Eating Disorders Association
Nonprofit organization dedicated to supporting individuals and communities affected by eating disorders
Go to source
If you are concerned that you or someone you know is showing signs of an eating disorder, you need to get help as soon as possible. Learn how to identify eating disorders, get help, and maintain your recovery over the long haul.
Getting Help for an Eating Disorder
Confide in someone you trust. The first step towards recovery for an eating disorder is often talking about it. Doing so can be frightening, but you will feel immensely relieved when you finally share with someone else. Choose someone who has always been supportive of you without casting judgment, maybe a best friend, a coach, a religious leader, a parent, or a school counselor. Set aside a time when you can talk to this person in private without interruptions. Try to be patient. Your loved one may be shocked, confused, or hurt that you have been suffering on your own all this time. Explain some of the symptoms you have noticed and when they started. You might also discuss the physical or emotional repercussions of your eating disorder, such as loss of a menstrual period or suicidal thoughts. Give this person some idea as to how they can help you. Would you like them to hold you accountable for eating right? Would you like this person to accompany you to the doctor? Let your loved one know how you can feel best supported.

Choose a specialist. After sharing news of your condition with a loved one, you will feel more confident and supported about seeking professional help. Your best hope for a full recovery lies in choosing a health care team that has experience treating eating disorders. You can find eating disorder specialists by asking for a referral from your family doctor, by calling local hospitals or medical centers, reaching out to your school counselor, or calling the National Eating Disorders Association's hotline at 1-800-931-2237.

Determine which treatment plan is best for you. Work with your doctor or counselor to figure out the type of treatment that will suit your situation. There is a variety of effective treatment options for eating disorders. Individual psychotherapy allows you to work one-on-one with a therapist to uncover some of the causes to your condition and to develop healthier ways of responding to triggers. One effective therapeutic approach is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on changing unhelpful thought patterns that influence your relationship with food and your body. Family therapy is helpful at guiding parents with useful tools on caring for a teenager with an eating disorder and bringing healthier lifestyle habits into the household for long term recovery. Medical monitoring is required so that your doctor can examine you physically to assure that you are regaining essential bodily functions as you progress through treatment. Your doctor might record your weight and perform regular tests. Nutritional counseling involves meeting with a registered dietitian on an ongoing basis to ensure that you are consuming adequate calories and macro-nutrients to maintain or return to a healthy weight. This professional will also work with you to change your relationship with food into a positive, healthy one. Medications are often prescribed when a co-occurring illness exists in addition to the eating disorder, such as depression. Common medications prescribed to help with eating disorder recovery include antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety meds, and mood stabilizers.
Try a combination of approaches for the best outcome. Your best hope for a long-lasting and successful recovery from eating disorders is with a combination of some type of therapy and medical care and nutritional counseling. Regardless, your treatment plan should be tailored to your unique needs, with any co-occurring illnesses factored in.

Find a support group. In the midst of your recovery, it can feel good to know that you are not alone. Finding a local support group through your treatment center or therapist's office can help you talk with others who are going through similar experiences and give you a source of support.
Maintaining Your Recovery

Challenge negative thoughts about your body. Negative thoughts can seem to rule your life when you are afflicted by an eating disorder. You might bully yourself about gaining an extra pound or criticize yourself for eating an entire meal as opposed to a partial serving. Overcoming these thought patterns is essential in your recovery. Use a few days to notice what you're thinking. Label certain thoughts as negative or positive, helpful or unhelpful. Think about how such thoughts might affect your mood or behavior. Combat negative, unhelpful thoughts by identifying if they are unrealistic. For example, if you find yourself thinking, “I will never get to a healthy weight,” you might ask yourself how you could possibly know such a thing. Can you predict the future? Of course not. Now that you have identified your unproductive thoughts, you can replace them with more helpful, realistic versions, such as, “It is taking me awhile to get to a healthy weight, but I can do it.”

Learn how to effectively fight stress. Stress can often serve as a trigger for the unhealthy behavior patterns that drive eating disorders. Therefore, developing positive methods for stress-management can help you maintain recovery. Some great ways to fight stress include: Get regular exercise. Sleep at least 7 to 9 hours each night. Get a hobby. Listen to music and dance. Spend time with positive, supportive people. Walk your dog. Take a long, relaxing bath. Learn how to say “no” when you've got too much on your plate. Release perfectionistic tendencies.

Develop a balanced diet and exercise plan. Eating and physical activity are an important part of overall health. However, people with eating disorders have unhealthy relationships with these things. You must work closely with your doctor and dietitian to determine a safe balance of exercise and a well-rounded diet that allows you to maintain optimal health.

Wear clothing that makes you feel comfortable. Aim to feel good about the clothing you wear. Select items that are flattering and comfortable to your current body size and shape rather than choosing clothes for your “ideal” body, or wearing clothing that completely hides your figure.

Give it time. Recovering from an eating disorder is a process. You may relapse several times before you successfully overcome the negative behavior patterns that drive your disorder. Keep at it. Don't give up. Recovery can be yours if you are persistent.
Identifying an Eating Disorder
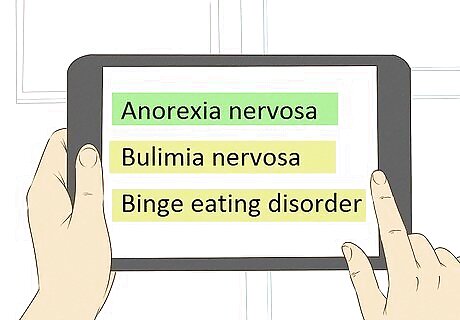
Research eating disorders. To inform yourself about the risk and seriousness of eating disorders, it can be helpful to perform a cursory internet search about these conditions. Only a doctor or mental health provider can officially diagnose your eating disorder, but learning more can help you understand how life-threatening these conditions can be, and motivate you to get help. Learn about the most common types of eating disorders. Anorexia nervosa is characterized by an obsessive preoccupation with body size and weight. An individual with this condition may fear gaining weight and believe they are overweight even when they're severely underweight. Individuals may refuse to eat and eat very restrictive diets. Some people with anorexia may purge (vomit) or take laxatives to lose weight. Bulimia nervosa involves periods of binge eating—that is, uncontrollably consuming large amounts of food—and then compensating for overeating by purging, taking laxatives or diuretics, exercising excessively, fasting, or a combination of these methods. This condition can be hard to spot because many people with bulimia maintain an average weight. Binge eating disorder is characterized by eating large amounts of food even when a person is not hungry. People with bulimia may eat in secret and be unable to control themselves during a binge. Although similar, individuals suffering from binge eating disorder (BED) do not engage in compensatory behaviors like purging or exercising excessively. People with BED may be overweight or obese.

Observe and document your symptoms. Once you learn more about eating disorders, you may notice several symptoms that describe your own behavior. Paying attention to your symptoms as well as your thoughts and feelings can be helpful when you seek professional help. You can log your symptoms in a journal to help you and your doctor better understand your eating disorder. Try to write in your journal daily, as this can help you spot the connections between your thought patterns and behaviors, which can be useful for your recovery treatment. For example, you might log an episode of binge-eating. Then, think back to what happened right before the episode. What were your thoughts? Feelings? Who were you around? What were you talking about? Then, log how you felt afterwards. What thoughts and feelings came over you?
Look for clues about how your disorder developed. It may be practical to think about when and how your symptoms began to appear. Pinpointing such details can help your doctor diagnose your condition and any co-existing conditions like anxiety or depression. Thinking about causes can also help when you start to make lifestyle changes during treatment. The exact cause of eating disorders is unknown. Still, researchers have found that many people have parents or siblings with eating disorders, and may have been raised with strong social or cultural ideals of thinness. They may also have low self-esteem and a perfectionist personality, and be subjected to images of thinness from peers or the media.



















Comments
0 comment