
views
X
Research source
Teach grammar effectively by knowing your students' needs; it is assumed that you already know the basics of teaching and learning styles.
Starting with Some Basic Rules

Teach singular and plural nouns. A singular noun is a word that describes one thing. Plural means that there are more than one thing. In most instances, add an ‘s’ to the end of the singular noun to make it plural. When teaching basic rules, mention that there are exceptions. But you don’t need to go into them at this point.

Teach pronouns. Pronouns are words that replace someone’s name. For example, Mary will become “she” and Harry will become “he.” These two together will become “they.” Continue with the other pronouns, such as “I,” “you,” “we,” “us,” and so on.

Teach how to conjugate verbs. Conjugating verbs is an essential skill to understanding how to make sentences match up. This involves making a verb match the subject. For example, when you have the verb “jump,” it will be conjugated as: “I jump,” “you jump,” he jumps,” and so on. Start with the present tense first and give the student lots of practice using this tense. Move onto past and future tense one at a time.
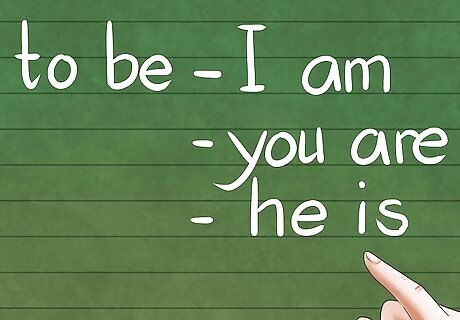
Teach a few irregular verbs. There are some irregular verbs that don’t follow the regular verb conjugation rules. One of these is “to be.” Teach this as: “I am,” “you are,” “he is,” and so on. Start with teaching the present tense first. Irregular verbs can be tricky. In addition, “to be” serves as a foundation for many other types of verb phrases. It’s important to master it before moving on.

Teach how to respond in the negative. If the student wants to disagree with something or say she did not do something, she will need to know how to construct that sentence. Show the student where to add “not” in a sentence. For example, you might say, “I am not jumping” or “I am not eating.”
Teaching More Advanced Activities
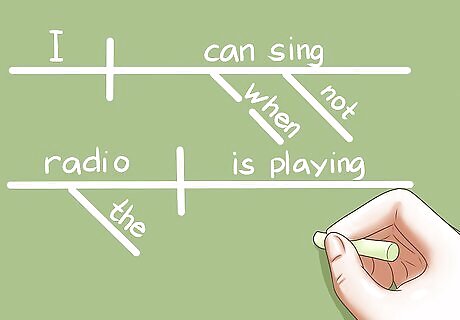
Teach how to diagram a sentence. Diagramming a sentence is a useful exercise to help students understand how sentences are constructed. Find the subject and predicate (verb) of the sentence. Find direct objects and indirect objects. Discuss which words alter the meaning of other words. Identify dependent and independent clauses.

Teach complex verb tenses. Once your students have grasped present, past and future verb tenses, introduce them to other types of verb conjugations. These might include present perfect simple, past progressive, present progressive, present conditional, past conditional, and so on.

Teach proper terminology. When you’re teaching beginning grammar, it might be better to use simple terms to describe concepts. As you teach more advanced grammar, you may choose to start introducing the proper terms that describe grammatical concepts.

Give quizzes that test students’ understanding. Periodically, assess your students’ learning with quizzes. This will give them a chance to put their knowledge to the test. This also gives you a chance to see how well they are learning the concepts. You will also see if concepts are confusing to students.
Teaching Effectively

Use examples to teach grammar. Take examples from sentences so that they make sense to the student. It is helpful to see how grammar rules are put into practice in different types of conversations or writings.

Build upon concepts that are familiar to the student. Explain grammatical rules by using concepts that the student already knows. For example, students will likely be familiar with verb tenses, such as past, present and future. Use these as ways to explain more complicated verb tenses.

Give students plenty of time to practice. Reinforce your lesson by giving the students lots of time to put their grammar knowledge to use. The point of learning grammar is to improve communication skills. Give your students the opportunity to practice frequently.
Make the instruction appropriate for your students. It is important to take note of your students’ learning levels, interests and styles. When you tailor your instruction to their level, they will be more invested in learning grammar. This will also reduce frustration and confusion for both the students and yourself.

Plan games and interesting activities. Grammar can be a dry subject if the teacher doesn’t engage the students effectively. Play games, plan conversation scenarios and do other activities that are appropriate and fun for the students.

Correct students in a positive way. Do not discourage your students by correcting their grammar in a way that reduces their desire to speak. Instead, correct errors by continuing the conversation and asking questions using the correct grammar. For example, your student says, “I catched the ball.” Don’t respond with “You mean, you caught the ball.” Instead, say, “You caught the ball? Did you score a point?” Continue the conversation with a gentle correction and an added question or comment.
Preparing to Teach

Know who your students are. In order to teach effectively, you need to know who your students are. You should also know what they want or need to learn from you. This will affect your teaching approach, as well as what you actually teach. For example, if you are teaching elementary school kids, you might focus on basic grammar rules that are easy to grasp. If you are teaching adults who are learning English as a second language, you might find these students to be older and highly motivated. They also may need immediate language skills.

Understand different learning styles. People learn in different ways depending on how they process information most effectively. Think about different styles of learning as you begin to plan how to teach grammar. Some of these learning styles include: Visual learning: These learners prefer reading and want to see what they’re learning. Auditory learning: These learners prefer to listen to instruction. Conversations and interactions are effective ways of teaching this learning style. Tactile learning: These learners prefer to touch and manipulate objects in order to learn about something. Kinesthetic learning: These learners move around a lot and benefit from getting up from a desk frequently.

Refresh your understanding of grammar rules. Take some time to go through a grammar guide or textbook. Even if you think you know grammar really well, spend some time refreshing your memory about different rules.

Pick out a textbook. You might choose to use a textbook as a guide for teaching. Choose one that is geared toward the same type of students that you will be teaching.
Choosing a Teaching Approach

Use the deductive approach if you want to explain quickly. The deductive approach of teaching grammar focuses on teaching certain grammar rules and then giving examples of that rule. It can be useful if you want to quickly explain grammar. It may be more useful with adult students. This approach can minimize student interaction and involvement. Clearly state what the rule allows and limits. Give a clear and brief explanation about what the grammar rule allows. Also describe what the rule does not allow. For example, always use “you were” and never use “you was.” Then follow up with an example of the rule. Illustrate the grammar rule with an example. You can use a simple sentence to illustrate it once. Then you might choose a more complicated sentence to demonstrate how the rule applies. Describe the rules with simplicity. Boil down the grammatical rules to simple terms. Try not to point out too many exceptions to the rule when you first introduce the rule.

Choose the inductive approach to allow students to explore language. The inductive approach allows students to discover how language and grammar works. Students learn grammar by making connections with their pre-existing understanding of language. For example, students learning English as a second language will learn to link English grammar rules to their native language grammar rules. This approach may allow for better memory retention of grammar. In addition, students are more autonomous learners. Don’t choose the inductive approach if you don’t have lots of time. Students need to work out a rule on their own by going through examples. Figuring out the rule may be at the expense of using the rule in practice. Give sentence examples that demonstrate differences. In order to help students pick out the rules, start with two sentences that have slightly different meanings. For example, write: “I have read every Stephen King book,” and “I read Stephen King’s latest book last week.” Ask the student to identify the difference between these two sentences.

Choose a functional approach to give students tools to communicate. The functional approach focuses on teaching grammar so that the students can function in their everyday lives. For example, what will they need to know so that they can go grocery shopping? How will they greet someone? Beginning students can learn complex concepts and use them in conversation. In this approach, it can be difficult to determine what aspects to focus on first.

Teach grammar through texts, stories and songs. Use examples of literature and popular writing to illustrate how grammar is used. This can be an effective way to teach grammar. Students can choose their own texts or stories that they’d like to use. This will make the lesson more interesting for the students. Students will also benefit from increased vocabulary. The texts can be difficult if they are too advanced for the student’s language level.

















Comments
0 comment