
views
Content

Make a list of all tools, materials, and responsibilities for the safety plan. This will help you determine what you need to include in your manual and also help you ensure that you don't forget anything critical. Depending on the nature of your business, you may need to produce a series of manuals, each of which focuses on a particular area. For example, if you have a company that uses a lot of chemicals, you will need sections about storage, handling, and transportation. If your company works in manufacturing, you might need sections about heavy machinery, handheld tools, safety goggles, and other items. Recruit the heads of every department to help you compile these lists.

Research the common standards in your industry. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) produce standards for areas such as risk management and food safety management. These standards provide a starting place for company safety manuals in these areas. You can find them online or by contacting these organizations. The ISO and similar organizations offer helpful guides about standards for production, food safety, and many other areas of specialization.

Look up your city and state guidelines to make sure you comply. Government organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) may require safety manuals for certain practices and procedures and may also stipulate what, at a minimum, the manual must cover. Contact your local city council to inquire about these guidelines and ask for a copy. Failure to follow these regulations, let alone not having a manual where one is required, may expose companies to lawsuits and in some cases, criminal charges.

Include a section on chemical safety if your company uses them. It's really important that you use chemicals exactly as they are intended. Make sure that your manual includes instructions on storage, usage, handling, and transportation. You can include separate sections on each of these topics. If you work in a scientific lab, you will need to make sure that all of your chemicals are properly labeled and kept at the correct temperatures, for example. Your manual should cover all of those protocols. Also cover information about how to transport chemicals to different parts of your building and to different buildings, if applicable.

Incorporate information on food safety if that applies to your business. Companies that make or serve food definitely need very thorough safety manuals. Make sure that your manual has sections on how to prepare the food, how to store it, and how to handle it. Include important charts about temperature guidelines and expiration dates. You should also include safety information about using professional-grade equipment like mixers and stoves.

Write a chapter on standard operating procedures regardless of your business. No matter what type of business you run, it's a good idea to let your employees know what to do in order to make sure they stay safe. You can write a safety manual that includes general safety tips and clearly explains what to do in case of an emergency. Consider including sections on events such as: Fire Natural disaster Active shooter Gas leak Power outage

Indicate who is responsible for each step in the safety plan. An important part of the manual is indicating who needs to do what. For every step you include, make sure to indicate who is responsible. When you are planning and researching the manual, decide who the best person is to handle each job. For example, if you are writing a section about making sure that chemicals are kept at the proper temperature, make sure to note that it is the on-duty supervisor's job to check that every hour.

Involve management in contributing to the content of the manual. While the actual writing may be contracted to a technical writer experienced in writing safety manuals, it will be more accepted within the company if management and employees are involved in its adoption. Encourage people to share their ideas on what safety aspects need to be covered. Ask managers to submit suggestions for different sections of the manual and how it should be organized. You could hold a meeting to gather feedback, send out an email, or even set up an anonymous survey for people to submit their responses. Solicit feedback from employees about what they need guidance on. Don't feel like you need to accept advice from everyone, but it won't hurt to open this up to all of your employees. Try giving everyone a chance to participate in a survey about what sort of information would be most helpful in the manual.
Format

Include a table of contents at the beginning. This is important no matter what type of business you run. Employees can check here to easily find whatever they are looking for. Make sure to make the section headings clear, brief, and include page numbers. You can include sections such as: Laboratory Safety Employee PPE Operating Procedures Cleaning Protocols Emergency Procedures Record Keeping

Include templates of commonly used documents for easy access. Your business probably requires that employees keep a lot of records, such as transportation and safety logs. You can keep templates of these forms in the manual so that your employees always know where to find them. This will be especially helpful if they have access to electronic copies of the manual. You could include an appendix in the safety manual that includes documents such as supply logs, cleaning schedules, and repair schedules. You can update these documents annually, or as often as needed.

Make electronic and paper copies that are updated annually. It's a good idea to keep both formats so that employees can always easily access the manual. Keep paper copies located throughout your business, especially in areas where they might come in handy. Areas where tools and chemicals are stored are good places to keep a manual visible. Keep an electronic version of the manual on your company website so that all employees can access it at any time. Standards and guidelines change, so make sure to review and update your manual each year. This way you will ensure that it is effective and relevant. You might not have to change anything, but it's a good idea to look it over to make sure that everything is current. The update process can include conducting regular safety audits, soliciting feedback from employees, and staying up to date with best practices and regulations in your industry.

Use language that is easy to understand. While outside regulators may examine the manual to ensure all appropriate regulations are covered, they will not read it day-in and day-out like your employees might need to. The manual should be written so they can easily understand and follow it. As you write, keep the following in mind: Use short sentences and short paragraphs with simple words. Write in the active voice.
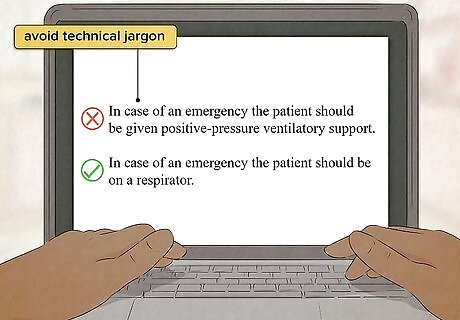
Avoid jargon so the manual is accessible to all employees. Try not to use complicated terms that only experts will understand. It's okay to use any necessary technical terms correctly, just make sure to give them context, and provide simple, clear definitions otherwise. Explain acronyms. You can either have an introductory section listing all acronyms with their definitions or introduce them in the text with the full term followed by its acronym in parentheses and using the acronym thereafter. Explain symbols. As with acronyms, you can have an introductory section or explain the symbols as they appear throughout the manual.

Lay out the manual to be easily read and understood. The layout should help the reader focus on the most important concepts and should be consistent throughout the manual. This will make it easy to understand the important safety information and will allow the reader to easily find what they are looking for. Try to keep the following in mind: Use headings and subheadings to introduce topics, identify subtopics, and group text blocks. Place drawings and the text that relates to them on the same page when possible.

Use a readable font style and point size for ease in reading. For printed body text, 10- to 12-point size is best, with a somewhat larger point size for headings. Subheadings can be the same point size as the body text but set off in boldface, italics, or both. Use black text on white paper for the best contrast between text and background. Shaded text boxes may be appropriate for callouts and sidebars as long as there is still sufficient contrast between the text and background.



















Comments
0 comment