
views
- The term “neurodivergent” describes a person whose brain develops or works differently from most people's brains.
- Neurodivergent conditions include autism, ADHD, learning disabilities (such as dyslexia), Down syndrome, Tourettes, and more.
- There is no “cure” for being neurodivergent, but it doesn’t need one! The different ways people communicate and express themselves are what make them unique.
What does “neurodivergent” mean?

Neurodivergent means your brain works differently from others due to a specific condition. Even though the term has been around since the 90s, it’s become more widely used on TikTok and other social media sites. Someone who is neurodivergent may have different strengths or challenges completing a task compared to another person. Rather than using words like “normal” or “abnormal” that are hard to define or could sound hurtful, “neurodivergent” is a much kinder term when you’re talking about someone with mental differences. Someone who isn’t considered neurodivergent is “neurotypical,” which means their brain works similarly to most other people's brains. “Neurodiversity” means that there is no single definition for “normal” thinking, learning, or behaving. According to the neurodiversity paradigm, these differences should be celebrated rather than looked down on.
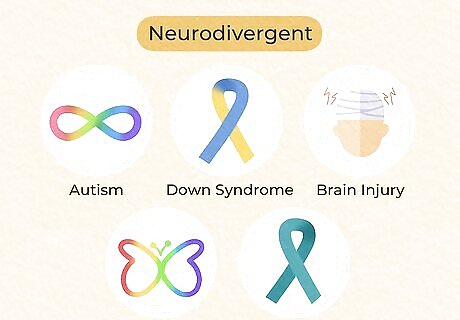
Many conditions, like autism and ADHD, are considered neurodivergent. Rather than being the label for a single condition, neurodivergent is an umbrella term for any brain-related difference that could affect how you learn, interact, or experience the world around you. While autism and ADHD are some of the more common examples, neurodivergence includes: Down syndrome Learning disabilities like dyslexia (difficulty with reading), dysgraphia (difficulty with writing), and dyscalculia (difficulty with math) Tourette’s syndrome (motor or vocal tics) Intellectual disability Brain injury Personality disorders Mental illnesses like social anxiety, depression, OCD, degenerative illnesses, and moreDid You Know? Neurodivergence involves diagnosable brain-related conditions. That means that things like personality traits (e.g. introversion) or conditions not affecting the mind (like asthma) don't make you neurodivergent. Many neurodivergent people can call themselves disabled.

The world isn't built with neurodivergent people in mind. Neurodivergent people have needs and skills that are different from those of the majority. If you're neurodivergent, you face barriers and obstacles that other people don't have to deal with. Creating a more inclusive and accessible world is important to help neurodivergent people flourish and live their best lives. Neurodivergent people may be able to get accommodations at school or work to help them reach their full potential. Accommodations help remove some barriers to give a person more equal access.
Signs of Neurodivergence

Recognize that everyone has different traits. "Neurodivergent" is a wide umbrella term covering an incredibly diverse group of people. Most neurodivergent people will relate to a few things on this list, but not all of them.

Differences in focus Do you have a hard time paying attention because you’re distracted or thoughts are racing through your head? Or do you get hyper-focused on a particular subject or individual details, losing sight of everything else in the moment? It could be a sign that you’re neurodivergent. Distractibility is specifically a sign of ADHD. People with ADHD tend to have the most pronounced focus issues. However, it's also common in learning disabilities.
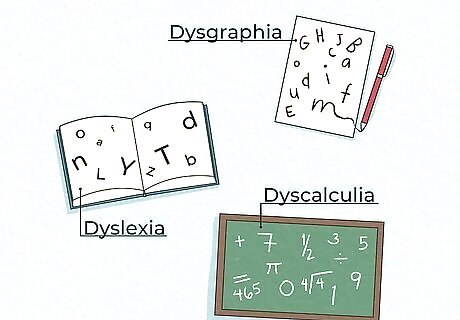
Trouble with reading, writing, or math Neurodivergent minds have different strengths and weaknesses. Your brain may struggle to process certain types of concepts, so it may take some extra time to understand the passage you’re reading or a problem you’re solving. You may have trouble putting words in the right order when you write or speak, or you may have trouble doing simple calculations in your head.. These are signs of specific learning disabilities, such as dyslexia and dyscalculia.
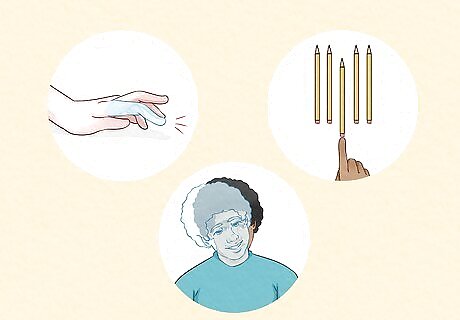
Repetitive behaviors Some neurodivergent people have repetitive behaviors that they can or can't control. Suppressing this behavior is often stressful, so in many cases, they're more comfortable when they can do what they need to do. Stimming and tics are two types of repetitive behavior. Stimming is another way to describe fidgeting. Examples include rocking, lining up pencils, shaking a leg, and humming. It can be automatic or on purpose. It helps people self-regulate so they can better manage feelings, focus, and sensory needs. It's common in autism, ADHD, and people with sensory processing issues. Tics are repetitive muscle movements like blinking, clicking fingers, or grunting. Much like a sneeze, they often can't be "held in" long. Tourette syndrome is the most common cause.
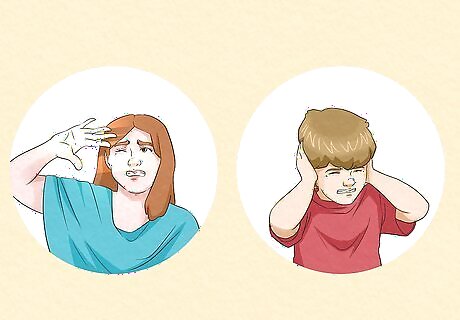
Strong responses to sensory input Do you get a little overwhelmed when you’re around loud noises, bright lights, or large groups of people? Some neurodivergent people have more sensitivity to intense stimuli, so they could feel uncomfortable or anxious if they’re put in these situations. Others may have reduced sensitivity, so they may seek out intense sensory input to help them regulate their nervous systems. If someone often struggles with this, they may be diagnosed with sensory processing disorder (SPD). You may also be sensitive to certain textures or objects, such as preferring a smaller spoon over a larger one or finding clothing tags uncomfortable. Some kids with sensory issues grow out of them. But for many neurodivergent people, SPD is a lifelong issue. While most people associate SPD with autism and ADHD, these aren't the only conditions it's associated with. It can also come with dyspraxia, PTSD, and more.

Struggling to communicate with others Some neurodivergent people find it a little tough to break the ice or maintain a conversation that they aren’t fully interested in. It may also be tougher to maintain eye contact, show emotion with your voice, or read non-verbal cues from the other person. In some cases, you may have trouble "reading between the lines" and understanding the nuances of what others are trying to say. Communication struggles aren't exclusive to autism. Issues like distractibility in ADHD or shyness in social anxiety can also affect socialization.

Preference for familiarity and anxiety about change Some neurodivergent people rely on routine to reduce stress and know what to expect throughout the day. Changes and unexpected things might feel disorienting and stressful. Habits might include eating the same meals, structured bedtime routines, or ordering the same food each time you visit a specific restaurant. Change to routine can feel overwhelming. Autistic people, people with Down syndrome, and people with anxiety disorders may rely on routines and sameness. Some specific personality disorders can also cause black-and-white thinking.

A unique way of looking at and solving problems When you think differently, you might come up with solutions that neurotypical people might miss. At work, teams with higher cognitive diversity are better at solving problems, and neurodiverse companies are more innovative. While thinking differently in a neurotypical world can sometimes be challenging, it can also give you an edge.
Creative and original thinking Creativity and a unique way of seeing the world are common in neurodivergent people. This can lead to strong skills in art, innovation, writing, or other fields of interest.

Powerful strengths Many different conditions come with different strengths as well as needs. For example, many autistic people are good at recognizing patterns and many people with ADHD are clear-headed in a crisis. You can read about common strengths for your specific condition(s).
How do you live well as a neurodivergent person?

Get an official diagnosis for more specific care plans. Even though some neurodivergent conditions share traits, it’s important to find the underlying cause so you find coping strategies that are the most effective. Talk openly to your doctor about what you’re experiencing and what you struggle with. They may run tests or recommend a screening from a specialist to diagnose what you have. Ask your doctor if there are any medicines you can take to help you with specific symptoms, such as to help you focus or feel less anxious. While the medication won’t completely eliminate your symptoms, they may be a bit easier to manage. Research specific conditions. Being neurodivergent is not a condition on it own, and doesn't tell you anything about what specific support you need. It is possible to have more than one neurodivergent condition, and having one can make you more likely to have another. For example, people with ADHD are more likely to be autistic and people with personality disorders are more likely to have anxiety.

Do soothing activities when you’re overwhelmed. When you’re feeling anxious or uncomfortable, remove yourself from the situation if you’re able to so you have some space. Take a moment to do something that’s relaxing and makes you feel calm, such as getting out into nature, visualizing a relaxing scene, listening to music, or journaling. When you feel your nerves start to go away, try to slowly reintroduce yourself into the situation again. Other activities you can try include exercising, drawing, stretching, or even just sitting next to a loved one in silence. Plan for extra relaxation time when you have a stressful event planned.

Tell other people about your needs. If there are specific ways that another person can support you, try to be direct about what you need from them. Clearly tell them what will help you complete a task or feel more comfortable so they’re aware of how you’re feeling. As you speak up more about your needs, it’ll be easier for others to adapt so they can clearly talk or interact with you. Example: If you have trouble focusing in class because of loud noises, you may tell a teacher that you need to wear noise-canceling headphones to drown out the noise. Example: If you’re overwhelmed in a large crowd, you may ask your friends to move to a different spot where you have a little more personal space.

Remind yourself it’s okay to not be perfect. If you’re getting frustrated with yourself for struggling with a task, take a second to close your eyes and tell yourself it’s okay. Rather than putting pressure on yourself to do something in the same way as a neurotypical person, practice some self-compassion and recognize all the hard work you’ve already done to get to this point. Don’t be afraid to try something different if you need to pivot. If what you’re doing already isn’t working, take a breath and brainstorm a new way to overcome the issue. Neurotypicals struggle with some things too based on their own skills and needs. The fact you may struggle more with certain things doesn't make you less important, nor does it diminish your strengths in other areas.

See a therapist to work through how to manage your condition. Make an appointment and let your therapist know what you’re experiencing and what condition you have. Your therapist will help you come up with specific strategies to use in your normal routine to set yourself up for success and when you’re feeling overwhelmed to help you calm down.

Network with other neurodivergent people, especially those with the same condition(s) as you. You aren't alone, and other people have similar experiences and struggles. It can help to hear from others who have minds like yours. Try joining an in-person group or online community full of people like you. They can offer advice, affirmations, and connection.



















Comments
0 comment