
views
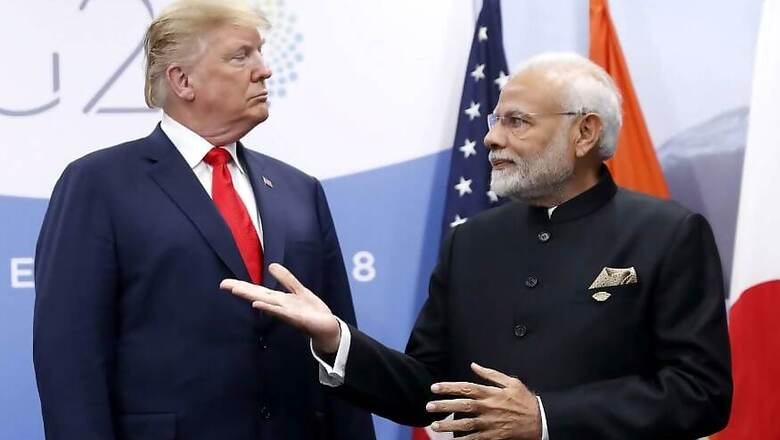
New Delhi: US President Donald Trump has said that he intends to end India's preferential trade treatment under generalised system of preferences (GSP) that allows $5.6 billion worth of Indian exports to enter the United States duty-free. Trump, who has vowed to reduce US trade deficits, has repeatedly called out India for its high tariffs.
What is GSP?
According to the Office of the United States Trade Representative, US trade preference programs such as the Generalised System of Preferences to provide opportunities for many of the world’s poorest countries to use trade to grow their economies and climb out of poverty.
It is a preferential tariff system extended by developed countries to developing countries. It is a preferential arrangement in the sense that it allows concessional low/zero tariff imports from developing countries.
Countries like the United States and United Kingdom, as well as the European Union give GSPs to imports from developing countries. GSP involves reduced/zero tariffs of eligible products exported by beneficiary countries to the markets of GSP-providing countries.
What is the objective of GSP?
The objective of GSP was to give development support to poor countries by promoting exports from them into the developed countries. According to the US Trade Representative Office (USTR), GSP promotes sustainable development in beneficiary countries by helping these countries increase and diversify their trade with the United States. “GSP provide opportunities for many of the world’s poorest countries to use trade to grow their economies and climb out of poverty," it reads.
According to the USTR, “GSP also boosts American competitiveness by reducing costs of imported inputs used by US companies to manufacture goods in the United States."
What is the impact of GSP withdrawal on India?
India had made a final plea for continuation of GSP benefits in August last year, arguing that the cheaper imports of intermediary products from India enable availability of cost-effective and price-competitive inputs to the US downstream industries and helps the US firms remain domestically and internationally competitive.
In its initial submission during the hearing, India had threatened to drag the US to the dispute settlement mechanism of the WTO, claiming withdrawal of the GSP benefits would be “discriminatory, arbitrary and detrimental" to its developmental needs.
In its post-hearing submission, while answering queries raised by the USTR GSP sub-committee and other US industry lobbies, India had maintained that GSP benefits are integral and catalytic in promoting the pace and sequence of domestic and external economic reforms in India.
US supermarket major Walmart in its submission to the USTR had come out in support of continuation of GSP programme for India, holding that it provides significant benefits to Walmart customers and US suppliers by reducing costs.
India exports nearly 50 products of the 94 products on which GSP benefits may be stopped. The GSP removal will leave a reasonable impact on India as the country enjoyed preferential tariff on exports worth of nearly $5.6 billion under the GSP route out of the total exports of $48 billion in 2017-18.
In total India exports nearly 1,937 products to the US under GSP.
Removal of GSP indicates a tough trade position by the US; especially for countries like India who benefited much from the scheme. The US was insisting that India reduce its trade surplus. India is the 11th largest trade surplus country for the US and India enjoyed an annual trade surplus of $21 billion in 2017-18.
What is the procedure for GSP in the case of the US?
Under GSP, there were zero/low concessional tariff on imports from developing countries. The US government selects a group of poor countries and a set of products and offers these countries lower-than-normal tariffs than it applies to imports from all other World Trade Organisation countries. The USTR makes annual reviews about the types of commodities to be selected under GSP and the countries to be benefited.
Which are the product groups covered under GSP?
The products covered under GSP are mainly agricultural products including animal husbandry, meat and fisheries and handicraft products. These products are generally the specialised products of the developing countries.
Who are the other beneficiaries under GSP?
The beneficiaries of GSP are around 120 developing countries. As on December 2018, India and Brazil were the major beneficiaries in terms of export volume realised under GSP. Imports from China and some developing countries are ineligible for GSP benefits. The beneficiaries and products covered under the scheme are revised annually.


















Comments
0 comment