views
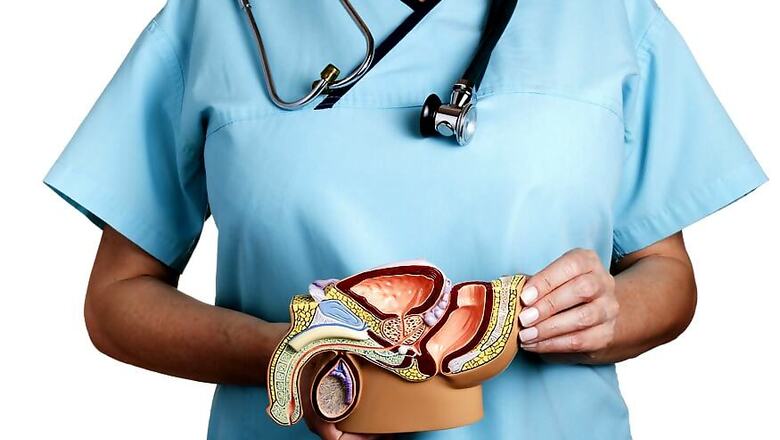
Cancer can be rightly called as the abnormal and unstoppable growth of cells, which often spreads into other tissues. Affecting one out of eight men, prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer found in men over the age of 50.
Cancer occurs in the prostate — a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Located at the base of the bladder, the prostate is the male reproductive organ that secretes prostate fluid. As we celebrate International Men’s Health Week 2019 from June 10 to 16, here is everything you should know about prostate cancer.
Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
While some of the signs of the early prostate cancer are burning sensation or pain during urination, difficulty while urinating, frequent urges to urinate at night, loss of bladder control, decreased flow or velocity of urine stream, blood in urine, also known as hematuria, presence of blood in semen, difficulty getting an erection or experiencing painful ejaculation.
However, when the prostate cancer spreads to the other parts, a man may experience pain in the back, hips, thighs, shoulders, or other bones, along with swelling or fluid buildup in the legs or feet, unexplained weight loss, fatigue and change in bowel habits.
Tests and diagnosis for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer can be tested through a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, which measures the level of PSA in the blood. Produced in the prostate gland, PSA is a protein that at an elevated level may be a sign of prostate cancer. Along with a PSA test, men can also be tested with a digital rectum exam (DRE). For the test, a clinician takes a sample of your blood and sends it to a lab for analysis.
Treatment of Prostate Cancer
While most of the prostate cancers do not require treatment, but a careful watching, the patient can be advised for treatment like radical prostatectomy, which is the surgical removal of the prostate gland, radiotherapy, hormone therapy and chemotherapy.


















Comments
0 comment