views
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in India with one woman being diagnosed every four minutes. It originates in the breast tissue when cells start growing abnormally and form a malignant lump or tumour. The abnormal cells can also spread to surrounding tissues and other parts of the body.
for the upcoming International Women’s Day. The
India is seeing a spurt in the cases of breast cancer among women, especially between 30 to 50 years of age. Deaths due to breast cancer can be reduced significantly through awareness about its symptoms and screening methodologies to enable early detection and treatment.
This International Women's Day, Dr. Rajeev Agarwal, Medanta Cancer Institute, explains how women should self-examine and consult a doctor due to occurrence of any warning signs of breast cancer, one of the most common cancer among women.
Why early screening?
Early and regular screening helps in systematic evaluation to detectan underlying cancer much before the manifestation of common symptoms. These symptoms include lump in the breast or underarm that persists post the menstrual cycle, a noticeable flattening or indentation on the breast, unusual discharge from the nipple that may be clear, bloody, or of another colour, redness or rashes around the nipple and swelling around the collarbone and armpit.If the cancer is detected at an early stage, it can be treated with minimum modalities, increasing the survival rate of the patient. Early detection through screening helps women resume their normal lives because the cancer can be best treated when the tumour is small. Therefore, breast cancer screenings should be made mandatory as part of annual medical check-ups to help curb the incidence of the disease in India.
Screening options
Breast self-examination (BSE)
It is not a screening guideline but is advised for early detection. It involves an examination of both breasts at regular intervals and aid the identification of any abnormality. Women must self-examine their breasts at least once a month post the age of 20 years. One should look for signs such as lumps or knots, discharge from the nipples and change in volume or shape of the breast.
Clinical breast examination
This is a physical examination conducted by a medical professional and should be undertaken once every three years. The areas of the breast and around the nipples which appear to be abnormal or irregular are monitored in a clinical breast examination.
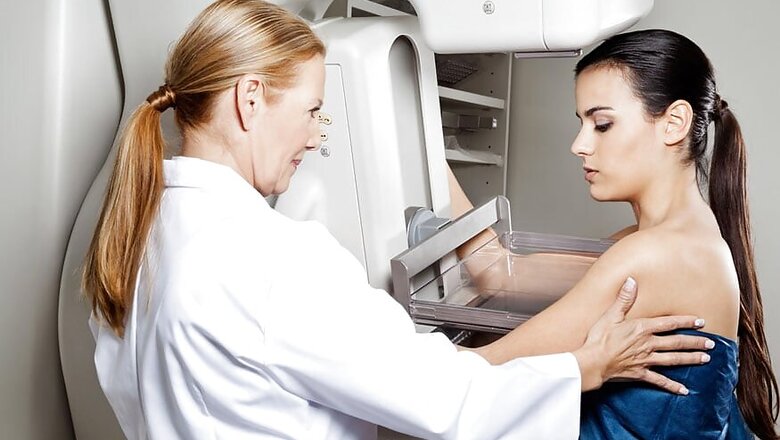
Mammography
While breast self-examination is an effective method for flagging off early warning signs, medical intervention must be sought post the age of 40 years. A mammography is the most common medical procedure for examining the breasts. It is an X-Ray which helps in tumor detection when the warning signs are not apparent.
Risk factors for breast cancer
•The risk for breast cancer increases with age and in most cases are diagnosed post 50 years
•Menstruation before the age of 12 years and menopause post the age of 55 years exposes women to hormones longer, increasing the risk
•Women with denser breasts are more prone to the disease as they have more connective tissue which may not be detected through a mammogram.
•Women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer once are more likely to get it for the second time
•Women with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer have a high risk
•Women who have undergone radiation therapy in the chest are more prone to the disease at a later stage
•Apart from the above, lack of physical activity, excessive consumption of alcohol and being overweight are also significant risk factors
Preventive screening recommendations
The screening protocol primarily depends on two factors- age of the individual and level of risk. Basis these, women are categorized into two groups- normal risk and increased risk and the guidelines vary for the two groups.
i. Women between 20- 40 years
For normal risk women in this age group, a clinical breast examination is recommended once every three years. Regular breast self-examination must also be done every month.Those having a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, must undergo an annual mammogram post the age of 35 years. Women with first or second-degree relatives with breast and ovarian cancers must begin their mammograms earlier, at the age of 25 years.
ii. Women above 40 years
For women above 40 years of age, annual clinical breast examination and mammography is recommended. Post the age of 50 years, mammography must be done once every two years. Regular breast self-examination must also be undertaken every month. For women who are at a high risk, an annual MRI of the breast is also recommended in addition to a mammogram.
Many women in India are largely unaware about the symptoms and screening recommendations for breast cancer.The need is to be self-aware and consult a medical expert well within time to understand the screening modalities. Early detection will lead to the cancer being nipped in the bud.



















Comments
0 comment