
views
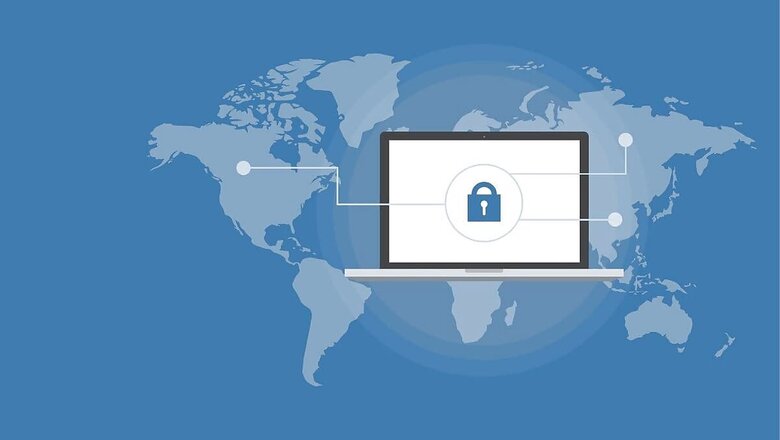
Two-Factor Authentication, multi-factor authentication, two-step verification – these are terms that you may have come across on the internet. Now, what is two-factor authentication, and why is it important? Two-factor authentication enables people to put an extra layer of security over their passwords for websites, social media platforms, services, and apps – usually verifying users via SMS or a pop-up notification, or an authenticator code, in case of third-party authenticator app. Now, there are various types of two-factor authentications that are available for people to leverage these days. Two-factor authentication forces people to provide at least two proofs of identity while accessing a service or a website on the internet, at least for the first time on a new or unknown device.
Two-factor authentication can be a combination of any of the two – password or PIN, fingerprint or other biometric ID (like Apple’s Face ID), verifying from a trusted smartphone that can generate or receive confirmation codes, or a hardware-based security device (like Google’s Titan Key). Further, there are two-factor authentication practices that are enabled by a website or a service that you are using, or there are specific tools that enable two-factor authentication for all apps and websites that a user visits on their smartphone or device.
Popular websites and services like Google, Gmail, Facebook, Twitter, and such have their own two-factor authentication techniques put in place for those who wish to use them. On the other hand, there are tools like Google’s Authenticator, Authy, Microsoft Authenticator and more, which enable 2FA by generating codes on a user’s smartphone or computer. Most services that support two-factor authentication (2FA) offer users a choice of authentication methods. Google and Microsoft, for example, can both either send a push notification to a trusted device, where users need to tap the notification to approve a sign in. Apart from that, services like Twitter, Facebook, and others use your phone number or a backup email to send a verification code, which the users can enter in order to successfully log in.
The most popular 2FA app out there is the Google Authenticator, which is available on both iOS and Android operating system. However, there are plenty of alternatives like Microsoft Authenticator, Authy, 1Password and the likes. All that these Authenticator apps require is a network connection during the initial setup. After that, everything that happens is on a user’s device. The process is most commonly governed by time-based one-time-passwords (OTPs).
Which Services Have Their Own 2FA Techniques
Google accounts, including both Gmail and Google Services offer a wide range of 2FA options. All Microsoft accounts, including Outlook, Xbox, Skype, etc, support a variety of authentication options, including Azure Active Directory accounts used with Microsoft’s business and enterprise services including Microsoft 365 and Office 365. 2FA support is very much prevalent among social media services like Facebook, Twitter, and the likes as well. Almost every online storage service supports 2FA, as well as most domain registrars and web hosting companies.
Setting Up two-Factor Authentication
Setting up 2FA on most services requires minimal to no technical knowledge or skill. As mentioned above, different types of 2FA techniques require different set-up methods. If you’re using SMS-based 2FA, all you need to do is link your mobile number with your account, configure the account to send a code to that number whenever you sign in on an untrusted device. For example, setting up two-factor authentication on Twitter requires users to first re-enter their password, then enter the phone number they want to receive the authentication code on. After this process is complete, users will receive the authentication code on their smartphone, entering the code will confirm that 2FA authentication is complete. Twitter itself keeps notifying users to set up 2FA for those who have not activated it.
Like Twitter, most of the websites and services that offer 2FA follow similar procedure to activate 2FA, if not exactly the same procedure.
To set up 2FA via an authenticator app, users first need to install the app on their smartphones. iOS users can download Google Authenticator from the Apple App Store. On Android devices, the app is available on the Google Play Store. The Microsoft Authenticator app is also available on both Apple App Store and Google Play Store and uses the same standard as Google Authenticator. Authy, the third most popular 2FA app is also available for both iOS and Android smartphones. In 1Password password manager, 2FA support is built into the app on all platforms.
Once you install an Authenticator app the next step is to set up the app to work with each account for which you want to enable 2FA.
The setup majorly requires users to enter a shared secret or a text string via the mobile app. Many apps also support using a camera to take a picture of a QR code, which contains the shared secret for your account. This is considered easier than entering an alphanumeric text string manually.
In order to set up an Authenticator app, users need to select the option to add a new account, select the bar code option, and then aim the smartphone camera at the bar code on the computer screen. The app will then fill in the necessary fields. After setting up the authenticator app, it begins generating codes based on the shared secret and the current time. To complete the setup procedure, users will need to enter the current code from the authenticator app. Once this is complete, users will need to enter the code displayed by the authenticator app every time they try to log in with a new device or web browser.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here


















Comments
0 comment