
views
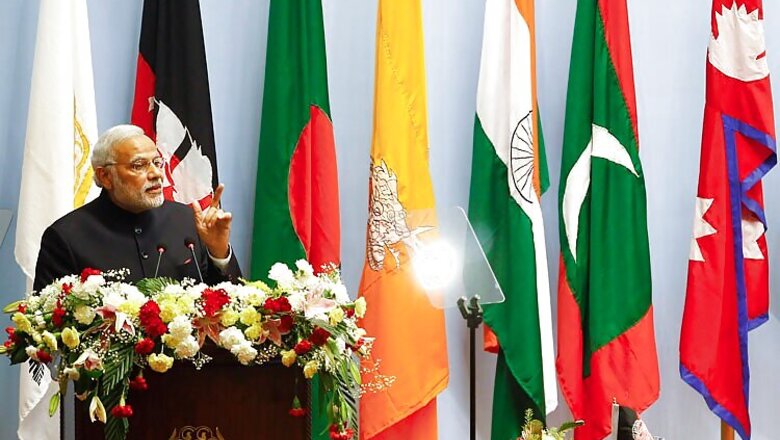
Building upon Prime Minister Narendra Modi's initiative of inviting all SAARC leaders to his swearing-in ceremony in May 2014, the neighbourhood continued to be the primary focus of India's foreign policy in 2015. While relations with Pakistan and Nepal remained on a tricky path, there was some forward movement in the ties with Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Bhutan, Maldives and Myanmar. Relations between India and Sri Lanka more or less maintained a status quo.
Nepal: It began with an upswing in the ties but the relationship were strained by the time the year came to an end. Bilateral ties with Nepal took a hit after the neighbouring country promulgated a new Constitution. India argued that the new Constitution did not take into account the concerns of all sections of the population, particularly the Madhesis who enjoy close ties with India. However, Nepal did not pay heed to India's protests and rebuked it for interfering in the country's internal affairs.
Earlier when Nepal was hit by a massive earthquake on April 25, India responded to the calamity and helped Nepal by launching its largest disaster response abroad, Operation Maitri. During External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj's visit to Kathmandu in June, India pledged $1 billion grant for the reconstruction of the quake-hit country.
Pakistan: Ties with Pakistan did not see any forward movement in the past one year despite two meetings between Modi and his Pakistani counterpart Nawaz Sharif. While pushing for better relations, India has maintained that talks are possible only in an atmosphere that is free of terror and violence.
Sharif and Modi first met on the sidelines of the BRICS summit in Ufa in Russia. The two sides unveiled a five-point agenda to address concerns on terrorism and to promote people-to-people contact. Despite a number of hurdles including on account of terror attacks in the aftermath of Ufa, and cancellation of initial round of NSA-level talks, a significant breakthrough was achieved in December with the NSAs meeting in Bangkok, followed by Swaraj's visit to Islamabad for the Heart of Asia Conference.
Bangladesh: Modi's visit to Bangladesh in June saw the exchange of instruments of ratification of the landmark land boundary agreement. It was a relief for over 50,000 people living in 162 enclaves across both countries as India and Bangladesh swapped enclaves, bringing to an end the 68-year-old boundary dispute. The June 6-7 visit of PM Modi also saw India-Bangladesh developmental cooperation scaling new heights, with India pledging a $2 billion Line of Credit for Bangladesh. The two countries took a host of steps to enhance trade and connectivity, including the launch of two new bus services. The two countries are a part of the sub-regional cooperation between Bangladesh, Bhutan, India and Nepal to enhance connectivity and regional integration.
Sri Lanka: Not much change taken place in the ties between India and Sri Lanka in the year gone by. Within months of the newly-elected Sri Lankan President Maithripala Sirisena taking charge of the island nation, two-way visits were held by the leaders and foreign ministers of the two countries. During Modi's visit to Sri Lanka in March, India pledged $318 million Line of Credit for railway upgradation (New Delhi's development assistance is already about $1.6 billion), unveiled a currency swap agreement of US $1.5 billion to help stabilise the Sri Lankan rupee and to develop Trincomalee as a regional petroleum hub with the cooperation of Lanka IOC (Indian Oil Corp's subsidiary in Sri Lanka) and Ceylon Petroleum Corporation.
Both countries also signed four pacts regarding visa exemption for official passport holders, youth exchanges, customs agreement (to address trade concerns and reduce non-tariff barriers) and the construction of the Rabindranath Tagore auditorium at the Ruhuna University with India's aid.
Afghanistan: Amid the backdrop of the unfolding transition in Afghanistan, India sustained its engagement with the war-torn country. During the visit of Afghan President Ashraf Ghani in April 2015, India reiterated its commitment to the reconstruction of the strife-torn country. The two sides focused on working towards a more liberalised business visa regime.
Afghanistan welcomed India's decision to extend the 1000 scholarships per year scheme by another 5 years as part of capacity building initiatives. India continues its assistance to the construction of the India-Afghanistan Friendship (Salma) Dam in Herat, expected to be completed in the first half of 2016. The Parliament Building in Kabul constructed with Indian assistance has already been completed as well as on the Doshi and Charikar power stations. But the resurgence of Taliban and Pakistan's continued support to the group remain a huge hindrance. Taliban has regained control of large swathes of land in Afghanistan in the last few months and is now in a position to threaten the elected government once again.
Bhutan: India's all-weather friendship with Bhutan continued on an upward curve. The visit of Bhutan's Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay to India in January focused on optimising cooperation in the field of hydropower – the centerpiece of economic cooperation between the two countries. The two sides reiterated their commitment to the 10,000 MW initiative and in this context, to the early implementation of the four JV-model projects, totaling 2120 MW.
Maldives: India also engaged with the Maldives leadership despite political volatility in the island country. This was reflected in the meeting between the foreign ministers of India and the Maldives on the sidelines of the UN summit in New York in September. External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj followed it up with a visit to the island nation from October 10-11 to reinvigorate ties.
Myanmar: Bilateral relations with Myanmar improved with the first India-Myanmar Joint Consultative Commission (JCC) meeting held in New Delhi on July 16, 2015. Steps were taken to further enhance the existing air connectivity, extending a $500 million Line of Credit to the Government of Myanmar for development priorities, and a commitment to enhance the regional and sub-regional cooperation under the BCIM-EC and the BIMSTEC framework. India also played an instrumental role in providing disaster relief support to Myanmar in response to widespread floods and landslides caused by Cyclone Komen.














Comments
0 comment