
views
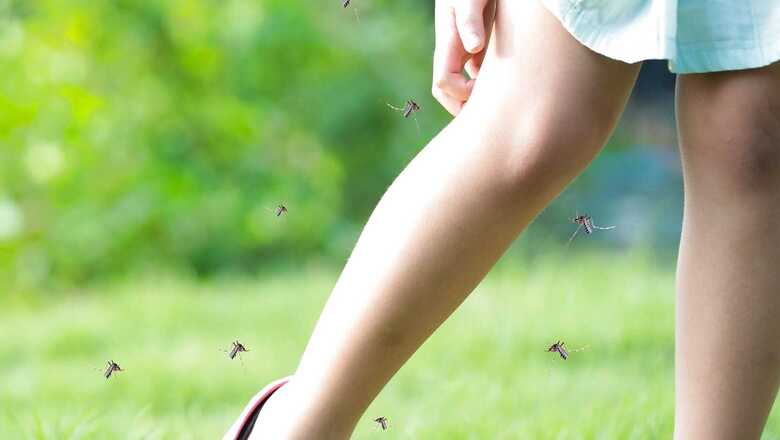
Monsoon can take a toll on human health. From manageable disease like cold and flu, to fatal diseases like dengue, malaria and chikungunya, monsoon brings along with it health complications that can put us at risk. While it might not be possible to avoid mosquito bites, as despite using ways like using mosquito repellents and avoiding mosquito-breeding, the vector succeeds in transmitting these diseases.
In a group, you must have noticed there is always someone who will complain about mosquitoes attacking them the most. That’s because, according to a report by Huff Post mosquitoes are selective insects, and some people are more likely to get bites than others.
There are certain factors which contribute to this effect. In one controlled study by the Journal of Medical Entomology, the bugs landed on people with blood Type O nearly twice as frequently as those with Type A. The researchers noted this has to do with secretions we produce, which tips mosquitoes off on a person’s blood type.
Entomology professor at the University of Florida, Jonathan F. Day said that more research needs to be conducted on mosquitoes’ potential preference for certain blood types over others. However, he agreed that mosquitoes do pick up on some cues we give off that make the bugs more likely to land on certain people.
“These cues let them know they are going to a blood source,” Day said. “Perhaps CO2 is the most important. The amount of CO2 you produce, like people with high metabolic rates ― genetic, other factors ― increases the amount of carbon dioxide you give off. The more you give off, the more attractive you are to these arthropods.”
The next question which pops up is what separates us from the nonliving entities that give off carbon dioxide, like cars? Mosquitoes look for primary cues in conjunction with what Day calls “secondary cues.”
Lactic acid — the stuff that causes our muscles to cramp during exercise — is one of those secondary cues, for example. Lactic acid is released through the skin, signaling to mosquitoes that we are a target, Day said.
Mosquitoes also have other qualities that help them pick up on secondary cues.
“Mosquitoes have excellent vision, but they fly close to the ground to stay out of the wind,” Day said. “They are able to contrast you with the horizon, so how you’re dressed matters. If you have on dark clothes, you are going to attract more because you’ll stand out from the horizon, whereas those wearing light colors won’t as much.”
A mosquito also takes in “tactile cues” once it has landed on you.
“Body heat is a really important tactile cue,” Day said. “That comes into play with genetic differences or physiological differences. Some people tend to run a little warmer — when they land, they’re looking for a place where blood is close to the skin.” That means those whose temperatures are a little higher are more likely to get the bite.
Lifestyle or other health factors may also play a role, said Melissa Piliang, a dermatologist at Cleveland Clinic. “If body temperature is higher, you’re exercising and moving around a lot, or if you’re drinking alcohol, you are more attractive to mosquitoes,” Piliang said. “Being pregnant or being overweight also increases metabolic rate.”
Huff Post also said that one study showed that people who consumed just one can of beer were more at risk of attracting mosquitoes than those who didn’t. Of course, drinking outside is a popular summer and fall activity. “If you’ve been moving around all day doing yardwork and then you stop around dusk and drink a beer on your patio, you’re definitely at risk of bites,” Piliang said.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Assembly Elections Live Updates here.


















Comments
0 comment