
views
X
Trustworthy Source
Mayo Clinic
Educational website from one of the world's leading hospitals
Go to source
But even the healthiest people can benefit from improving air circulation and removing pollutants from the air at home. We’ll show you how to increase oxygen levels in your home, get more oxygen into your body, and offer an overview of some common medical equipment used to treat low oxygen, as well as an overview of blood oxygen levels in general.
- Improve the oxygen levels in your home by opening a window for about 10 minutes at a time. Or, step outside for 10 minutes to get a quick boost.
- Introduce house plants like orchids or succulents to boost oxygen levels in your home, and run an air purifier to filter out air pollutants.
- Get more oxygen immediately by inhaling through your nose for 2 seconds, and exhale through pursed lips for 4 seconds. Repeat this for 10 minutes.
Increasing Oxygen in Your Home
Open your windows to increase airflow in your home. One of the simplest and fastest ways to increase the oxygen in your home—and in your body—is to open a few windows around the house. Open 2-3 windows to give the air someplace to enter and exit and create some steady airflow. Leave them open for 5-10 minutes at a time, and open them again when the house starts to feel stuffy. If you live in a cold or polluted area, consider cracking your windows instead, to let air in without overwhelming your home with cool temperatures or pollution. If you have outdoor allergies, consider installing clean air window screens that filter out birch pollen, grass pollen, and ragweed to help you enjoy fresh air without giving yourself an allergic reaction. Also, close doors to your closets, pantries, and other areas that don’t lead anywhere to help air move throughout your house without it getting trapped.
Run an air filter to remove indoor air pollutants. Both permanent and portable air filters help to remove pollutants from the air in your home and circulate that air, making for a fresher environment that may facilitate easier breathing. When selecting an air filter, take the following into consideration: How much money you want to spend—it may be worth it to spend more on a quality filter. The MERV rating (minimum efficiency reporting value) – the higher the MERV rating, the better quality the air filter. Read user reviews to get an idea of how well they work and how often they have to be replaced.
Introduce oxygen-producing indoor plants to your home. Houseplants are useful in converting carbon dioxide to oxygen, and are a natural and aesthetically pleasing way to freshen up the air in your home. For the most effective setup, aim to have 1 houseplant per 100 sq ft (9.3 m) of space. If you have limited room, put plants in the rooms you use the most, like your bedroom and kitchen. The following plants may be especially efficient: Areca palm Lady palm Bamboo palm Rubber plant Dracaena English ivy Dwarf date palm Ficus Boston fern Peace lily If you have pets, make sure your selected plants are non-toxic and pet-safe.
Install extractor fans and have your home’s HVAC inspected. If you don’t have them, contact an HVAC contractor to install an extractor fan over your stove and in your bathroom. These suck moist and bad-smelling air out of your house, helping to improve ventilation and keeping the air in your home fresh. In addition, ask a contractor to inspect your home’s built-in ventilation system, which may not be working as it should if your home is constantly stuffy or hard to breathe in. Make sure you clean the fans every few months with warm water and a degreasing solution, especially in the kitchen. Clean them as often as suggested in the user guide that comes with your fan.
Getting More Oxygen Into Your Body
Step outside to get some fresh air. Getting out into the fresh air does wonders for your respiratory system and increases your blood oxygen levels. If you can perform some light exercises and get your blood pumping and lungs working, all the better. Aim to walk or sit outside for at least 10 minutes a day, or whenever you feel you need more air, to keep your body healthy and happy. If you’re unable to go outside, sit by an open window to enjoy some fresh air indoors.
Practice simple breathing exercises to take in more oxygen. Performing breathing exercises helps to make each breath more effective. For example, to perform pursed lip breathing, first relax your shoulders and neck muscles. Then inhale through your nose for 2 seconds. Purse your lips like you’re about to blow a kiss, then exhale for 4 seconds. Perform this exercise 5 times a day for 5-10 minutes at a time. Also try deep belly breathing: Place a hand on your stomach and feel it expand as you inhale for 10 seconds through your nose, then exhale for 10 seconds through your mouth, and repeat for 15 minutes.
Drink a glass of water to move oxygen through your body. Water itself carries vital oxygen throughout our body and helps raise blood oxygen levels by delivering it to your cells and organs. Adult men need about 15.5 cups (3.7 L) of water per day, and adult women need about 11.5 cups (2.7 L). Carry a bottle and sip some water throughout the day to stay properly hydrated and oxygenated. Beware beverages like “oxygenated water” that claim to offer more oxygen to your cells. Plain water already has oxygen, and any added oxygen these beverages contain is mostly lost the moment you open the bottle.
Lie on your belly to help your body take in more oxygen. Lying prone and face-down prevents your heart and stomach from putting pressure on your lungs, and allows your lungs to fully expand. For a quick solution, try lying on your stomach, placing pillows under your head, chest, knees, or feet to get comfy. Keep that position for 1-2 hours, or as long as is comfortable. This position may also help you intake more oxygen throughout the night.

Quit smoking and vaping to help your lungs function. It’s one of the most important and beneficial lifestyle changes you can make. Only 2-3 weeks after a person quits smoking, their circulation, and therefore their blood oxygen levels, improve significantly. After 9 months, they have less shortness of breath and can breathe much more efficiently. Even vaping and smoking marijuana interferes with healthy lung activity and can inhibit proper blood oxygen levels.
Using Medical Equipment to Get More Oxygen
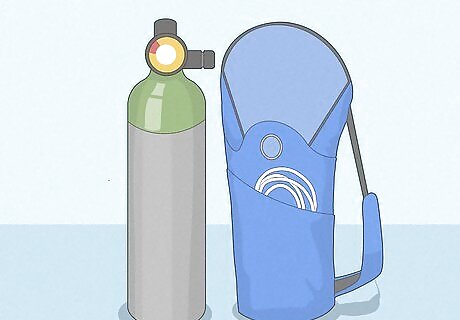
Portable oxygen tanks Oxygen comes in portable, lightweight units that are easy to carry around the house with you. Ask your doctor about a prescription for an oxygen tank. They may perform some lung function tests and prescribe you the appropriate amount of oxygen. Place the small clear nosepiece (nasal cannula) inside your nostrils to get oxygen straight from the tank. Oxygen therapy at home should be used with caution, especially when treating Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Always follow instructions given by your physician. Always follow safety precautions when using oxygen: Do not smoke, apply heat, or have any sort of fire near your oxygen containers. Depending on your symptoms and your doctor’s recommendations, you might use oxygen all the time or only while you’re exercising or sleeping. Oxygen intake should be carefully monitored at all times when the tank is being used. Medical equipment is only appropriate for people with specific illnesses. Consult your doctor to see if these options are right for you.
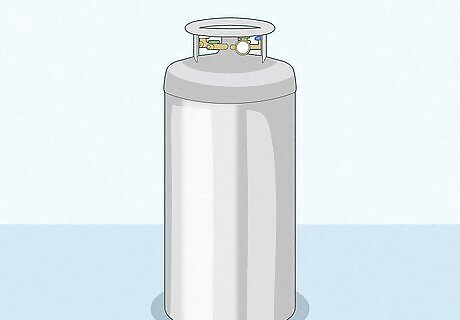
Compressed gas or liquid oxygen If you only need high-flow oxygen while you’re at home, you might have gas or liquid oxygen delivered from a reputable provider. Ask your doctor to help you choose a type of oxygen, or contact your health insurance company to ask if they have a preferred provider. Oxygen can come to your home as compressed gas in a tank or cylinder, or as a liquid. Liquid oxygen is more portable, but the tanks do not last as long.
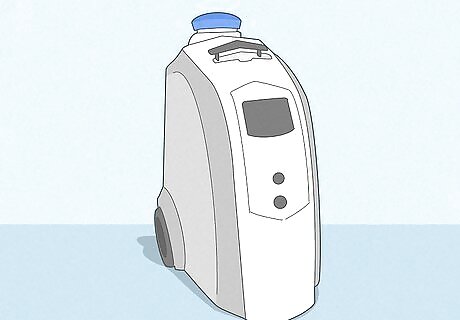
Oxygen concentrators Oxygen concentrators plug into an outlet and continuously filter oxygen from your environment, channeling it to you through a face mask or nasal cannula. Using an oxygen concentrator is a good option if you need lots of concentrated oxygen while at home due to a chronic illness. Ask your doctor if one is right for you—your doctor can suggest a suitable machine, and a nurse will set it up and show you how to use it.
About Blood Oxygen Levels
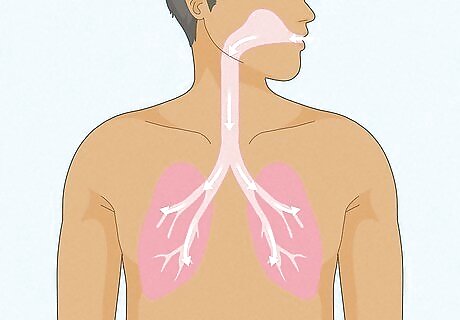
Blood oxygen level is the amount of oxygen in your blood. Oxygen enters your body every time you inhale, and your lungs pass the oxygen into your bloodstream, where it’s transported to cells and organs that need it to function. Blood oxygen level is a measurement of how much of this oxygen is currently in your blood. Everyone needs a certain amount to ensure their bodies function properly. Some people with certain respiratory disorders or diseases like COPD may have a harder time getting oxygen into their bloodstream and need assistance through doctor-recommended treatments.

Blood oxygen levels are measured with a pulse oximeter device. A pulse oximeter is a small device that’s secured to your finger. After a few moments, the display shows how much oxygen you have in your blood. It’s painless and easy. Alternatively, a doctor may draw blood to be tested in a lab for more insight into the workings of your respiratory system. A normal blood oxygen level is between 95% and 100% oxygen saturation, though this may be lower for patients with COPD or other respiratory conditions.


















Comments
0 comment